Effectiveness of Ultrasound-Guided Retrolaminar Block and Erector Spinae Plane Block in Retroperitoneal Laparoscopic Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 35370419
- PMCID: PMC8974250
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S349028
Effectiveness of Ultrasound-Guided Retrolaminar Block and Erector Spinae Plane Block in Retroperitoneal Laparoscopic Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Purpose: Retrolaminar block (RLB) and erector spine plane block (ESPB) share a similar block site, but their analgesia principle may differ. This study compared the postoperative analgesic effects of ultrasound-guided RLB and ESPB for retroperitoneal laparoscopic surgery.
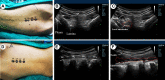
Patients and methods: The study included patients who scheduled for laparoscopic nephrectomy from July 2020 to January 2021. Patients in RLB group received a three-point block at the posterior surface of T8-T10 lamina, and those in ESPB group received at the T9 level. The primary result was the score of visual analogue scale (VAS). Secondary results included information on intraoperative and postoperative analgesia consumption and rescue analgesia usage, skin temperature, serum interleukin (IL)-1β, prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) level and the occurrence of safety events.
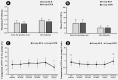
Results: There was no significant difference between the two groups in the postoperative VAS scores at both the rest and cough state (All P>0.05). The skin surface temperature of the affected side and the healthy side in ESPB group was higher than that in the RLB group at the end of the surgery (P=0.002) and after surgery (P=0.016). The RLB group had a higher ephedrine usage than the ESPB group (P=0.027). Compared with the ESPB group, the RLB group had a shorter time to exhaust (P=0.045) and lower serum IL-1β level (P=0.049). Patients in neither group developed severe adverse event.
Conclusion: Ultrasound-guided RLB and ESPB can provide safe and effective postoperative analgesia for retroperitoneal laparoscopic surgery. ESPB has more stable intraoperative hemodynamics, while RLB has more potential research value for patients' rapid recovery.
Keywords: anesthetics; laparoscopy; nerve block; perioperative care.
© 2022 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Analgesic efficacy of ultrasound-guided retrolaminar block in truncal surgeries: A narrative review.J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2024 Oct-Dec;40(4):557-563. doi: 10.4103/joacp.joacp_137_23. Epub 2024 Jul 19. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39759058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Erector spinae plane block versus retrolaminar block for postoperative analgesia after breast surgery: a randomized controlled trial.J Anesth. 2021 Feb;35(1):27-34. doi: 10.1007/s00540-020-02855-y. Epub 2020 Sep 11. J Anesth. 2021. PMID: 32915300 Clinical Trial.
-
[Efficacy of erector spinae block versus retrolaminar block for postoperative analgesia following posterior lumbar surgery].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2019 Jun 30;39(6):736-739. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2019.06.17. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2019. PMID: 31270055 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Analgesic Efficacy Comparison Between Ultrasound-Guided Erector Spinae Plane Block and Retrolaminar Block in Patients Undergoing Modified Radical Mastectomy: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Cureus. 2024 Dec 21;16(12):e76124. doi: 10.7759/cureus.76124. eCollection 2024 Dec. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39835025 Free PMC article.
-
Analgesic efficacy and safety of erector spinae plane block in breast cancer surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Anesthesiol. 2021 Feb 20;21(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12871-021-01277-x. BMC Anesthesiol. 2021. PMID: 33610172 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Erector spinae plane block for laparoscopic surgeries: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Anesthesiol. 2024 Oct 29;24(1):389. doi: 10.1186/s12871-024-02775-4. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 39472781 Free PMC article.
-
Thoracolumbar Retrolaminar Block: Anatomical and Radiological Study of Injectate Pattern Distribution in Canine Cadavers.Animals (Basel). 2023 Sep 25;13(19):3008. doi: 10.3390/ani13193008. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835614 Free PMC article.
-
Analgesic efficacy of ultrasound-guided retrolaminar block in truncal surgeries: A narrative review.J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2024 Oct-Dec;40(4):557-563. doi: 10.4103/joacp.joacp_137_23. Epub 2024 Jul 19. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39759058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retrolaminar block for opioid-free anaesthesia and enhanced recovery after posterior lumbar discectomy: A randomised controlled study.Indian J Anaesth. 2024 Mar;68(3):261-266. doi: 10.4103/ija.ija_773_23. Epub 2024 Feb 22. Indian J Anaesth. 2024. PMID: 38476544 Free PMC article.
-
NEW CONCEPT OF FUSION TECHNICS IN REGIONAL ANESTHESIA.Acta Clin Croat. 2022 Sep;61(Suppl 2):135-144. doi: 10.20471/acc.2022.61.s2.18. Acta Clin Croat. 2022. PMID: 36824627 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Clayman RV, Kavoussi LR, Soper NJ, et al. Laparoscopic nephrectomy. N Engl J Med. 1991;324(19):1370–1371. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

