Deep Learning-based Artificial Intelligence Improves Accuracy of Error-prone Lung Nodules
- PMID: 35370462
- PMCID: PMC8964321
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.69400
Deep Learning-based Artificial Intelligence Improves Accuracy of Error-prone Lung Nodules
Abstract
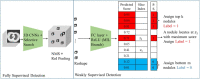
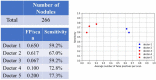
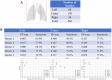
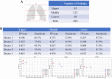
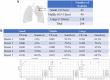
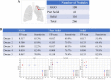
Introduction: Early detection of lung cancer is one way to improve outcomes. Improving the detection of nodules on chest CT scans is important. Previous artificial intelligence (AI) modules show rapid advantages, which improves the performance of detecting lung nodules in some datasets. However, they have a high false-positive (FP) rate. Its effectiveness in clinical practice has not yet been fully proven. We aimed to use AI assistance in CT scans to decrease FP. Materials and methods: CT images of 60 patients were obtained. Five senior doctors who were blinded to these cases participated in this study for the detection of lung nodules. Two doctors performed manual detection and labeling of lung nodules without AI assistance. Another three doctors used AI assistance to detect and label lung nodules before manual interpretation. The AI program is based on a deep learning framework. Results: In total, 266 nodules were identified. For doctors without AI assistance, the FP was 0.617-0.650/scan and the sensitivity was 59.2-67.0%. For doctors with AI assistance, the FP was 0.067 to 0.2/scan and the sensitivity was 59.2-77.3% This AI-assisted program significantly reduced FP. The error-prone characteristics of lung nodules were central locations, ground-glass appearances, and small sizes. The AI-assisted program improved the detection of error-prone nodules. Conclusions: Detection of lung nodules is important for lung cancer treatment. When facing a large number of CT scans, error-prone nodules are a great challenge for doctors. The AI-assisted program improved the performance of detecting lung nodules, especially for error-prone nodules.
Keywords: CT images; artificial intelligence; lung nodules.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Effects of Artificial Intelligence Assistance on the Radiologists' Assessment of Lung Nodules on CT Scans: A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2023 May 18;12(10):3536. doi: 10.3390/jcm12103536. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37240643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Performance of Deep-learning-based Artificial Intelligence on Detection of Pulmonary Nodules in Chest CT].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2019 Jun 20;22(6):336-340. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2019.06.02. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31196366 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Lung Nodule Detectability of Artificial Intelligence-assisted CT Image Reading in Lung Cancer Screening.Curr Med Imaging. 2022;18(3):327-334. doi: 10.2174/1573405617666210806125953. Curr Med Imaging. 2022. PMID: 34365951
-
Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy of Lung Nodules in Chest Computed Tomography Using Artificial Intelligence: Retrospective Analysis.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Jan 27;27:e64649. doi: 10.2196/64649. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 39869890 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence-based deep learning algorithms for ground-glass opacity nodule detection: A review.Narra J. 2025 Apr;5(1):e1361. doi: 10.52225/narra.v5i1.1361. Epub 2025 Mar 5. Narra J. 2025. PMID: 40352244 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Effects of Artificial Intelligence Assistance on the Radiologists' Assessment of Lung Nodules on CT Scans: A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2023 May 18;12(10):3536. doi: 10.3390/jcm12103536. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37240643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research trends of artificial intelligence and radiomics in lung cancer: a bibliometric analysis.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Dec 5;14(12):8771-8784. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-1316. Epub 2024 Nov 13. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 39698627 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging diagnostics of pulmonary ground-glass nodules: a narrative review with current status and future directions.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Aug 1;14(8):6123-6146. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-674. Epub 2024 Jul 18. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 39144060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Thorough Review of the Clinical Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Mar 4;17(5):882. doi: 10.3390/cancers17050882. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40075729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Errors in Radiology: A Standard Review.J Clin Med. 2024 Jul 23;13(15):4306. doi: 10.3390/jcm13154306. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39124573 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liu J, Cao L, Akin O. et al. Accurate and robust pulmonary nodule detection by 3D feature pyramid network with self-supervised feature learning. arXiv. 2019;1907:11704.
-
- Morozov SP, Gombolevskiy VA, Elizarov AB. et al. A simplified cluster model and a tool adapted for collaborative labeling of lung cancer CT scans. Comput Meth Prog Bio. 2021;206:106111. - PubMed
-
- Chikontwe P, Kim M, Nam SJ, Multiple instance learning with center embeddings for histopathology classification. MICCAI. 2020.
-
- Ilse M, Tomczak J, Welling M. Attention-based deep multiple instance learning. ICML. 2018.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

