Analysis of Ionizing Radiation Induced DNA Damage by Superresolution dSTORM Microscopy
- PMID: 35370480
- PMCID: PMC8966514
- DOI: 10.3389/pore.2021.1609971
Analysis of Ionizing Radiation Induced DNA Damage by Superresolution dSTORM Microscopy
Abstract
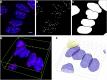
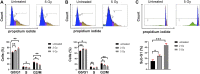
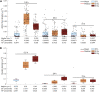
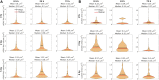
The quantitative detection of radiation caused DNA double-strand breaks (DSB) by immunostained γ-H2AX foci using direct stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (dSTORM) provides a deeper insight into the DNA repair process at nanoscale in a time-dependent manner. Glioblastoma (U251) cells were irradiated with 250 keV X-ray at 0, 2, 5, 8 Gy dose levels. Cell cycle phase distribution and apoptosis of U251 cells upon irradiation was assayed by flow cytometry. We studied the density, topology and volume of the γ-H2AX foci with 3D confocal microscopy and the dSTORM superresolution method. A pronounced increase in γ-H2AX foci and cluster density was detected by 3D confocal microscopy after 2 Gy, at 30 min postirradiation, but both returned to the control level at 24 h. Meanwhile, at 24 h a considerable amount of residual foci could be measured from 5 Gy, which returned to the normal level 48 h later. The dSTORM based γ-H2AX analysis revealed that the micron-sized γ-H2AX foci are composed of distinct smaller units with a few tens of nanometers. The density of these clusters, the epitope number and the dynamics of γ-H2AX foci loss could be analyzed. Our findings suggest a discrete level of repair enzyme capacity and the restart of the repair process for the residual DSBs, even beyond 24 h. The dSTORM superresolution technique provides a higher precision over 3D confocal microscopy to study radiation induced γ-H2AX foci and molecular rearrangements during the repair process, opening a novel perspective for radiation research.
Keywords: DNA-DSB; confocal microscopy; dSTORM; ionizing radiation; superresolution; γ-H2AX.
Copyright © 2021 Brunner, Varga, Bozó, Polanek, Tőkés, Szabó, Molnár, Gémes, Szebeni, Puskás, Erdélyi and Hideghéty.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

