The Effectiveness of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Post-stroke Dysphagia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35370584
- PMCID: PMC8967953
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.841781
The Effectiveness of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Post-stroke Dysphagia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) applied to the mylohyoid cortical region has positive clinical effects on post-stroke. Therefore, we conducted a meta-analysis to investigate the efficacy of rTMS for patients with post-stroke dysphagia.
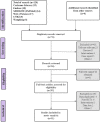
Methods: According to PRISMA guidelines, we searched the databases of MEDLINE (PubMed), Cochrane Library, Embase, Web of Science, CNKI, Wangfang. We searched for studies of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of rTMS to treat dysphagia after stroke and screened by inclusion and exclusion criteria. Features of RCTs were extracted. The heterogeneity of the trials was measured by I 2 statistic.
Results: In total, 11 RCTs with 463 dysphagia patients fulfilled our inclusion criteria. In our analysis, rTMS demonstrated a great beneficial effect for post-stroke dysphagia when combined with traditional swallowing exercises. Moreover, a greatly significant difference (P = 0.008) was noted based on stimulation frequency (high frequency vs. low frequency). Additionally, no significant difference (P = 0.53) was observed based on stimulation site (affected vs. unaffected hemisphere).
Conclusions: Overall, rTMS can effectively accelerate the improvement of swallowing function in patients with post-stroke swallowing disorders.
Keywords: dysphagia; effectiveness; meta-analysis; repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation; stroke.
Copyright © 2022 Wen, Liu, Zhong, Peng, Wang, Liu and Gong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Comment in
-
Commentary: The effectiveness of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for post-stroke dysphagia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Hum Neurosci. 2022 Dec 1;16:1018885. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.1018885. eCollection 2022. Front Hum Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36530198 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Cheng I. K. Y., Chan K. M. K., Wong C. S., Li L. S. W., Chiu K. M. Y., Cheung R. T. F., et al. . (2017a). Neuronavigated high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for chronic post-stroke dysphagia: a randomized controlled study. J. Rehabil. Med. 49, 475–481. 10.2340/16501977-2235 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

