Emodin Protects Against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury via the JNK/Nur77/c-Jun Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 35370650
- PMCID: PMC8968870
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.717271
Emodin Protects Against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury via the JNK/Nur77/c-Jun Signaling Pathway
Abstract
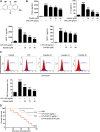
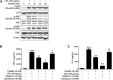
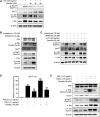
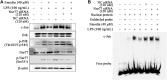
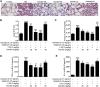
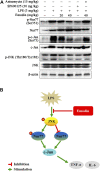
Background: Acute lung injury (ALI) is a serious inflammatory disease with clinical manifestations of hypoxemia and respiratory failure. Presently, there is no effective treatment of ALI. Although emodin from Rheum palmatum L. exerts anti-ALI properties, the underlying mechanisms have not been fully explored. Purpose: This study aimed to investigate the therapeutic effect and mechanism of emodin on LPS-induced ALI in mice. Methods: RAW264.7 cells and zebrafish larvae were stimulated by LPS to establish inflammatory models. The anti-inflammatory effect of emodin was assessed by ELISA, flow cytometric analysis, and survival analysis. In vitro mechanisms were explored by using Western blotting, luciferase assay, electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA), and small interfering RNA (siRNA) approach. The acute lung injury model in mice was established by the intratracheal administration of LPS, and the underlying mechanisms were assessed by detecting changes in histopathological and inflammatory markers and Western blotting in lung tissues. Results: Emodin inhibited the inflammatory factor production and oxidative stress in RAW264.7 cells, and prolonged the survival of zebrafish larvae after LPS stimulation. Emodin suppressed the expression levels of phosphorylated JNK at Thr183/tyr182 and phosphorylated Nur77 at Ser351 and c-Jun, and increased the expression level of Nur77 in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells, while these regulatory effects of emodin on Nur77/c-Jun were counteracted by JNK activators. The overexpression of JNK dampened the emodin-mediated increase in Nur77 luciferase activity and Nur77 expression. Moreover, the inhibitory effect of emodin on c-Jun can be attenuated by Nur77 siRNA. Furthermore, emodin alleviated LPS-induced ALI in mice through the regulation of the JNK/Nur77/c-Jun pathway. Conclusions: Emodin protects against LPS-induced ALI through regulation on JNK/Nur77/c-Jun signaling. Our results indicate the potential of emodin in the treatment of ALI.
Keywords: JNK/Nur77/c-Jun; acute lung injury; emodin; inflammation; lipopolysaccharide.
Copyright © 2022 Xie, Yan, Zhou, Cao, Zheng, Lu, Yang, Ma, Chen, Huo, Tian, Liu and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Liquiritin exhibits anti-acute lung injury activities through suppressing the JNK/Nur77/c-Jun pathway.Chin Med. 2023 Apr 3;18(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s13020-023-00739-3. Chin Med. 2023. PMID: 37013552 Free PMC article.
-
Liang-Ge-San, a classic traditional Chinese medicine formula, attenuates acute inflammation in zebrafish and RAW 264.7 cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Mar 1;249:112427. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112427. Epub 2019 Nov 25. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31778782
-
Emodin alleviated pulmonary inflammation in rats with LPS-induced acute lung injury through inhibiting the mTOR/HIF-1α/VEGF signaling pathway.Inflamm Res. 2020 Apr;69(4):365-373. doi: 10.1007/s00011-020-01331-3. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Inflamm Res. 2020. PMID: 32130427
-
Aloe-emodin from rhubarb (Rheum rhabarbarum) inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 macrophages.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 May 14;153(3):846-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.03.059. Epub 2014 Mar 29. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24685589
-
Emodin Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Injury via Down-Regulation of miR-223 in H9c2 Cells.Int Heart J. 2019 Mar 20;60(2):436-443. doi: 10.1536/ihj.18-048. Epub 2019 Feb 8. Int Heart J. 2019. Retraction in: Int Heart J. 2022;63(1):190. doi: 10.1536/ihj.63.190. PMID: 30745529 Retracted.
Cited by
-
Single-cell RNA-Seq analysis of molecular changes during radiation-induced skin injury: the involvement of Nur77.Theranostics. 2024 Sep 9;14(15):5809-5825. doi: 10.7150/thno.100417. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 39346541 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine attenuates inflammation and organ injury partially by upregulating Nur77 in sepsis.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 Jun;11(6):e883. doi: 10.1002/iid3.883. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 37382273 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of Active Compound of Terminalia catappa L. Extract and Its Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties by Regulating Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Cellular Signaling Pathways.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Oct 28;34(10):2118-2131. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2407.07044. Epub 2024 Sep 2. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39252640 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of potential biomarkers and pathways involved in high-altitude pulmonary edema using GC-MS and LC-MS metabolomic methods.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):30978. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82047-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39730680 Free PMC article.
-
Systematically investigate the mechanism underlying the therapeutic effect of emodin in treatment of prostate cancer.Discov Oncol. 2025 Mar 27;16(1):413. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02141-x. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40148580 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonta P. I., van Tiel C. M., Vos M., Pols T. W., van Thienen J. V., Ferreira V., et al. (2006). Nuclear Receptors Nur77, Nurr1, and NOR-1 Expressed in Atherosclerotic Lesion Macrophages Reduce Lipid Loading and Inflammatory Responses. Arterioscler Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 26, 2288–2294. 10.1161/01.ATV.0000238346.84458.5d - DOI - PubMed
-
- Catalán Ú., Fernández-Castillejo S., Anglès N., Morelló J. R., Yebras M., Solà R. (2012). Inhibition of the Transcription Factor C-Jun by the MAPK Family, and Not the NF-Κb Pathway, Suggests that Peanut Extract Has Anti-inflammatory Properties. Mol. Immunol. 52, 125–132. 10.1016/j.molimm.2012.05.007 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cui H., Li S., Xu C., Zhang J., Sun Z., Chen H. (2017). Emodin Alleviates Severe Acute Pancreatitis-Associated Acute Lung Injury by Decreasing Pre-B-cell colony-enhancing Factor Expression and Promoting Polymorphonuclear Neutrophil Apoptosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 16, 5121–5128. 10.3892/mmr.2017.7259 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

