Efficacy and Mechanism of Buyang Huanwu Decoction in Patients With Ischemic Heart Failure: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial Combined With Proteomic Analysis
- PMID: 35370712
- PMCID: PMC8971676
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.831208
Efficacy and Mechanism of Buyang Huanwu Decoction in Patients With Ischemic Heart Failure: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial Combined With Proteomic Analysis
Abstract
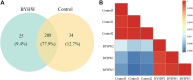
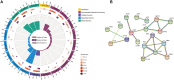
Objective: Buyang Huanwu Decoction (BYHW), a famous herbal prescription in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), has been used for 200 years for treating ischemic heart failure (IHF). This study aims to assess the efficacy and safety of BYHW combined with guideline-guided pharmacotherapy in patients with IHF and explore the biological mechanism by which BYHW exerts its efficacy. Methods: In the multicenter, double-blind, randomized controlled trial, a total of 80 patients with IHF were randomized to receive BYHW or placebo for 3 months. The primary efficacy endpoints were New York Heart Association (NYHA) classification, TCM syndrome scores, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-ProBNP), whereas the mechanism exploration endpoints included energy metabolism parameters and coagulation function parameters. In addition, we performed the proteomic study of the serum of patients after treatment by label-free quantification technology to verify the candidate target proteins and pathways. Results: After 3 months of treatment, the NYHA classification, TCM syndrome scores, and the percentage of subjects with at least 30% reduction in NT-ProBNP were significantly improved in the BYHW group, compared with the control group (p < 0.05); BYHW treatment also significantly regulated blood glucose, blood lipid levels, ameliorated energy metabolism and improved coagulation function parameters. There were no significant differences in safety endpoints between the two groups. In addition, we obtained 56 differentially expressed proteins by proteomics, including 20 upregulated proteins and 36 downregulated proteins. Bioinformatic analysis revealed the mechanism of BYHW treatment was significantly related to complement and coagulation cascades, cholesterol metabolism, NF-kappa B signaling pathway, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, and metabolic pathways. Among these differentially regulated proteins, fibrinogen gamma (FGG), fibrinogen beta (FGB), Carboxypeptidase B2 (CPB2), Coagulation factor XIII A (F13A1), Intercellular adhesion molecule1 (ICAM1), Apolipoprotein C-II(APOC2), Apolipoprotein C-I(APOC1), and CD44 were found to be signature proteins associated with the efficacy of BYHW against IHF. Conclusion: BYHW treatment can further improve cardiac dysfunction and clinical symptoms in IHF based on standard therapy without apparent adverse effects. Additionally, BYHW may play a therapeutic role in IHF by improving energy metabolism and regulating coagulation function through multiple targets and pathways.
Keywords: Buyang Huanwu decoction; coagulation function; energy metabolism; ischemic heart failure; proteomics; randomized controlled trial.
Copyright © 2022 Zhu, Wei, Li, Wang, Ren, Li, Ma, Wang, Qiao, Zhou and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer MW declared a shared parent affiliation with the author(s) YL, JR, BM, and JL to the handling editor at the time of review.
Figures


Similar articles
-
To explore the regulatory effect of Buyang Huanwu Decoction on cerebral infarction based on quantitative proteomics.J Proteomics. 2023 Apr 15;277:104850. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2023.104850. Epub 2023 Feb 20. J Proteomics. 2023. PMID: 36813112 Clinical Trial.
-
[Quantitative proteomic research of biological basis of Buyang Huanwu decoction therapy for cerebral infarction combined with Qi-deficiency and blood-stasis syndrome].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2018 Jun;43(11):2199-2206. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20180423.001. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29945368 Chinese.
-
Analysis of the mechanism of Buyang Huanwu Decoction against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion by multi-omics.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Apr 6;305:116112. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.116112. Epub 2022 Dec 26. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36581164
-
Comparison of Traditional Chinese Medicine in the Long-Term Secondary Prevention for Patients with Ischemic Stroke: A Systematical Analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 18;12:722975. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.722975. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34867326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Buyang Huanwu decoction for the rehabilitation of ischemic stroke patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2021 Mar 9;19(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12955-021-01728-6. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2021. PMID: 33750396 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroprotective effect of Astragali Radix on cerebral infarction based on proteomics.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jun 9;14:1162134. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1162134. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37361203 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of Wuhu oral liquid in treating acute soft tissue injuries: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, parallel-controlled trial.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 23;15:1335182. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1335182. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38464733 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Naoxintong Capsule on Microglia and Proteomics of Cortex After Myocardial Infarction in Rats.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 May;61(5):2904-2920. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03724-x. Epub 2023 Nov 10. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 37948003
-
Traditional Chinese medicine for cardiovascular disease: efficacy and safety.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Dec 3;11:1419169. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1419169. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39691499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrating multi-omics and machine learning strategies to explore the "gene-protein-metabolite" network in ischemic heart failure with Qi deficiency and blood stasis syndrome.Chin Med. 2025 Jul 17;20(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s13020-025-01151-9. Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40671145 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cardiovascular Society Heart Failure Group of Chinese Medical Association (2018). Heart Failure Professional Committee of Chinese Medical Doctor Association, and Editorial Committee of Chinese Journal of Cardiology Chinese Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Heart Failure 2018. Chin. J. Cardiol. 46, 760–789. 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2018.10.004 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

