Corticospinal Excitability Is Lower During Eccentric Than Concentric Cycling in Men
- PMID: 35370788
- PMCID: PMC8966379
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.854824
Corticospinal Excitability Is Lower During Eccentric Than Concentric Cycling in Men
Abstract
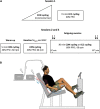
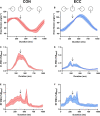
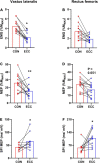
How corticospinal excitability changes during eccentric locomotor exercise is unknown. In the present study, 13 volunteers performed 30-min strenuous concentric and eccentric cycling bouts at the same power output (60% concentric peak power output). Transcranial magnetic and electrical femoral nerve stimulations were applied at exercise onset (3rd min) and end (25th min). Motor-evoked potentials (MEPs) amplitude was measured for the rectus femoris (RF) and vastus lateralis (VL) muscles with surface electromyography (EMG) and expressed as a percentage of maximal M-wave amplitude (MMAX). EMG amplitude 100 ms prior to MEPs and the silent period duration were calculated. There was no change in any neural parameter during the exercises (all P > 0.24). VL and RF MMAX were unaffected by exercise modality (all P > 0.38). VL MEP amplitude was greater (26 ± 11.4 vs. 15.2 ± 7.7% MMAX; P = 0.008) during concentric than eccentric cycling whereas RF MEP amplitude was not different (24.4 ± 10.8 vs. 17.2 ± 9.8% MMAX; P = 0.051). While VL EMG was higher during concentric than eccentric cycling (P = 0.03), RF EMG showed no significant difference (P = 0.07). Similar silent period durations were found (RF: 120 ± 30 ms; VL: 114 ± 27 ms; all P > 0.61), but the silent period/MEP ratio was higher during eccentric than concentric cycling for both muscles (all P < 0.02). In conclusion, corticospinal excitability to the knee extensors is lower and relative silent period longer during eccentric than concentric cycling, yet both remained unaltered with time.
Keywords: M-wave; knee extensor muscles; motor-evoked potential; silent period; transcranial magnetic stimulation.
Copyright © 2022 Clos, Mater, Legrand, Poirier, Ballay, Martin and Lepers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Barbero M., Merletti R., Rainoldi A. (2012). Atlas of Muscle Innervation Zones: Understanding Surface Electromyography and Its Applications. New York: Springer Science & Business Media.
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

