A Case Series of Ketoacidosis After Coronavirus Disease 2019 Vaccination in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes
- PMID: 35370952
- PMCID: PMC8971718
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.840580
A Case Series of Ketoacidosis After Coronavirus Disease 2019 Vaccination in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes
Abstract
Introduction: We report a case series of severe ketoacidosis after COVID-19 vaccination in a type 1 diabetes patients treated with insulin and an SGLT-2 inhibitor.
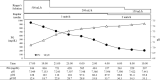
Case report: We present two cases of type 1 diabetes mellitus. One patient was treated with insulin therapy and an SGLT-2 inhibitor, and the other patient was treated with insulin therapy alone. Both patients became ill after coronavirus disease-2019 vaccination, making it difficult to continue their diet or insulin injections. On admission, they developed severe diabetic ketoacidosis. This is the first report of ketoacidosis after coronavirus disease-2019 vaccination.
Conclusion: The vaccine should be carefully administered to type 1 diabetes patients receiving intensive insulin therapy and a sodium-glucose transporter due to the high risk ketoacidosis. It is important to instruct patients to drink sufficient fluids and to continue insulin injections when they become sick.
Keywords: clinical diabetes; coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination; ketoacidosis; latent autoimmune diabetes in adults; sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor; type 1 diabetes.
Copyright © 2022 Yakou, Saburi, Hirose, Akaoka, Hirota, Kobayashi, Awane, Asahi, Amagawa, Ozawa, Ohno and Matsushita.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Yamada T, Shojima N, Noma H, Yamauchi T, Kadowaki T. Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter-2 Inhibitors as Add-on Therapy to Insulin for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Diabetes Obes Metab (2018) 20(7):1755–61. doi: 10.1111/dom.13260 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical