Effects of Antidiabetic Drugs on Endothelial Function in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35370959
- PMCID: PMC8969579
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.818537
Effects of Antidiabetic Drugs on Endothelial Function in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: The changes of endothelial function in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients are closely associated with the development of cardiovascular disease (CVD). However, it is still unclear whether commonly used antidiabetic drugs can improve endothelial function. Flow-mediated dilation (FMD) is a noninvasive tool for evaluating endothelial function, which typically examines changes in the brachial artery diameter in response to ischemia using ultrasound. We performed a network meta-analysis (NMA) to explore the associations between changes in endothelial function and antidiabetic drugs by evaluating FMD in T2DM patients.
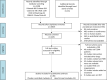
Methods: We systematically searched several electronic databases for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published from inception until January 25, 2022 with no language restriction. The primary outcome was FMD change in all studies, and we performed subgroup analysis in T2DM patients without CVD. NMA was performed to calculate the mean differences (MDs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
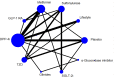
Results: From the 1,987 candidate articles identified in the initial search, 30 RCTs were eventually included in the analysis. In all studies, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonists [MD = 3.70 (1.39-5.97)], TZD [MD = 1.96 (0.006-3.89)] produced improvement of FMD change compared to lifestyle intervention. GLP-1R agonists [MD = 3.33 (1.36-5.34) and MD = 3.30 (1.21-5.43)] showed significantly greater improvements in FMD change in pairwise comparisons with sulfonylureas and placebo. SGLT-2i also showed efficacy compared to sulfonylureas (MD = 1.89, 95% CI, 0.10, 3.75). In studies of T2DM patients without CVD, GLP-1R agonists [MD = 3.53 (1.24-5.76)], and TZD [MD = 2.30 (0.27-3.24)] produced improvements in FMD change compared to lifestyle treatment. GLP-1R agonists [MD = 3.25 (1.13-5.40), and MD = 3.85 (1.68-6.13)] showed significantly greater improvements in pairwise comparisons with sulfonylureas, and placebo.
Conclusion: In T2DM patients, both GLP-1R agonists, SGLT-2i and TZD have favorable effects to improve endothelial function in T2DM patients. In T2DM patients without CVD, GLP-1R agonists had a greater effect to improve endothelial function than sulfonylureas. These suggested that GLP-1R agonists are associated with significantly improved endothelial function in T2DM patients.
Keywords: antidiabetic drugs; diabetes; endothelial function; flow-mediated dilation; meta-analysis; type 2.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Yao, Wang, Liu, Zhang, Zhao, Hu, Guan and Lyu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists and sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors for people with cardiovascular disease: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 25;10(10):CD013650. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013650.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34693515 Free PMC article.
-
Dipeptidyl-peptidase (DPP)-4 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1 analogues for prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its associated complications in people at increased risk for the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 10;5(5):CD012204. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012204.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28489279 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of new hypoglycemic drugs on cardiac remodeling: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023 Jun 9;23(1):293. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03324-6. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023. PMID: 37296380 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Adjuvant Treatment with Empagliflozin or Semaglutide Increases Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Subjects with Well-Controlled Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Jan 15;47(1):54. doi: 10.3390/cimb47010054. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39852169 Free PMC article.
-
A Non-Coronary, Peripheral Arterial Atherosclerotic Disease (Carotid, Renal, Lower Limb) in Elderly Patients-A Review PART II-Pharmacological Approach for Management of Elderly Patients with Peripheral Atherosclerotic Lesions outside Coronary Territory.J Clin Med. 2024 Mar 5;13(5):1508. doi: 10.3390/jcm13051508. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38592348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive treatment of diabetic endothelial dysfunction based on pathophysiological mechanism.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Feb 28;12:1509884. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1509884. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40093018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Therapeutics for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-A Look at the Past Decade and a Glimpse into the Future.Biomedicines. 2024 Jun 21;12(7):1386. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071386. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39061960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of first-line antidiabetic drugs on the improvement of arterial stiffness: A Bayesian network meta-analysis.J Diabetes. 2023 Aug;15(8):685-698. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.13405. Epub 2023 May 10. J Diabetes. 2023. PMID: 37165762 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous