Global Proteomic Analyses Reveals Abnormal Immune Regulation in Patients With New Onset Ankylosing Spondylitis
- PMID: 35371008
- PMCID: PMC8967996
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.838891
Global Proteomic Analyses Reveals Abnormal Immune Regulation in Patients With New Onset Ankylosing Spondylitis
Abstract
Background: Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disease with serious consequences and a high rate of morbidity and mortality, In our previous work, we reveal the key features of proteins in new-onset ankylosing spondylitis patients.
Material and methods: Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the spine, and inflammation plays an essential role in AS pathogenesis. The inflammatory process in AS, however, is still poorly understood due to its intricacy. Systematic proteomic and phosphorylation analyses of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were used to investigate potential pathways involved in AS pathogenesis.
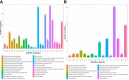
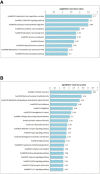
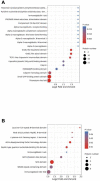
Results: Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis was performed and discovered 782 differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) and 122 differentially phosphorylated proteins (DPPs) between 9 new-onset AS patients and 9 healthy controls. The DEPs were further verified using parallel reaction monitoring (PRM) analysis. PRM analysis verified that 3 proteins (HSP90AB1, HSP90AA1 and HSPA8) in the antigen processing and presentation pathway, 6 proteins (including ITPR1, MYLK and STIM1) in the platelet activation pathway and 10 proteins (including MYL12A, MYL9 and ROCK2) in the leukocyte transendothelial migration pathway were highly expressed in the PBMCs of AS patients.
Conclusion: The key proteins involved in antigen processing and presentation, platelet activation and leukocyte transendothelial migration revealed abnormal immune regulation in patients with new-onset AS. These proteins might be used as candidate markers for AS diagnosis and new therapeutic targets, as well as elucidating the pathophysiology of AS.
Keywords: ankylosing spondylitis (AS); global proteomic; immune regulation; peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC); phosphorylation.
Copyright © 2022 Yu, Hong, Zhang, Zheng, Liu, Xu, Zhu, Cai, Liu, Yin, Hu, Tang and Dai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Quantitative Proteomic Analyses To Reveal the Key Features of Proteins in New Onset Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients.ACS Omega. 2020 Aug 3;5(32):20153-20161. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c01776. eCollection 2020 Aug 18. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 32832769 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Ankylosing Spondylitis by iTRAQ.Clin Transl Sci. 2015 Oct;8(5):579-83. doi: 10.1111/cts.12265. Epub 2015 Mar 19. Clin Transl Sci. 2015. PMID: 25788137 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of fatty acid oxidation in the ligament as a contributing factor of ankylosing spondylitis: A comparative proteomic study.J Proteomics. 2015 Jan 15;113:57-72. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2014.09.014. Epub 2014 Oct 2. J Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 25281561
-
Late-onset ankylosing spondylitis and related spondylarthropathies: clinical and radiological characteristics and pharmacological treatment options.Drugs Aging. 2005;22(6):451-69. doi: 10.2165/00002512-200522060-00001. Drugs Aging. 2005. PMID: 15974637 Review.
-
Differentially expressed protein-coding genes in ankylosing spondylitis: Emerging insights into pathogenesis and therapeutic approaches.Int J Rheum Dis. 2023 Aug;26(8):1440-1452. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.14814. Epub 2023 Jul 5. Int J Rheum Dis. 2023. PMID: 37403943 Review.
Cited by
-
HSP90β promotes osteoclastogenesis by dual-activation of cholesterol synthesis and NF-κB signaling.Cell Death Differ. 2023 Mar;30(3):673-686. doi: 10.1038/s41418-022-01071-3. Epub 2022 Oct 5. Cell Death Differ. 2023. PMID: 36198833 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring hub pyroptosis-related genes, molecular subtypes, and potential drugs in ankylosing spondylitis by comprehensive bioinformatics analysis and molecular docking.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023 Jun 29;24(1):532. doi: 10.1186/s12891-023-06664-8. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023. PMID: 37386410 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics signatures associated with hip arthropathy in ankylosing spondylitis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 May 14;12:1556118. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1556118. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40438364 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative proteomic screening uncovers candidate diagnostic and monitoring serum biomarkers of ankylosing spondylitis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2023 Apr 11;25(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03044-4. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37041650 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative proteomic analysis reveals the molecular mechanism of the Yesso scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis) in response to Polydora infection.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Nov 2;20:5966-5977. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.10.043. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 36382199 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

