High Expression of MicroRNA-200a/b Indicates Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
- PMID: 35371343
- PMCID: PMC8975693
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2751696
High Expression of MicroRNA-200a/b Indicates Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
Abstract
Objective: To detect the expression levels of microRNA-200a/b (miR-200a/b) in tumor tissues and serum of patients with epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) and to explore its clinical significance.
Methods: A retrospective selection of 30 cases of benign ovarian disease or healthy physical examination (control group) and 55 cases of EOC patients. Real-time quantitative PCR was used to detect the expression level of miR-200a/b in tumor tissues and serum, and the miR-200a/b expresses relevance in the two types of samples were evaluated at the same time. Receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) and Kaplan-Meier survival analysis were used to evaluate the diagnostic value of miR-200a/b expression and its influence on prognosis, respectively.
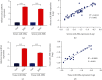
Results: The serum and tissue miR-200a/b expression levels in EOC patients were higher than those in the control group (P < 0.001), and there was a significant positive correlation between serum and tissue miR-200a/b expression (R 2 = 0.9419, P < 0.001 and R 2 = 0.9605, P < 0.001). ROC analysis showed that the expression of serum miR-200a/b can distinguish EOC patients from the control group. In addition, there were significant differences in the TNM stage, tumor differentiation, and lymph node metastasis between the miR-200a/b high- and low-expression groups (P < 0.05). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis found that the overall survival and disease-free survival of patients with high miR-200a/b expression were shorter than those of patients with low miR-200a/b expression (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Upregulation of miR-200a/b expression is a common molecular event in EOC patients, and miR-200a/b can be used as a noninvasive biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of EOC.
Copyright © 2022 Beilei Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Diagnostic and prognostic relevance of circulating exosomal miR-373, miR-200a, miR-200b and miR-200c in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 29;7(13):16923-35. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7850. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26943577 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA-200a/c as potential biomarker in epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC): evidence based on miRNA meta-signature and clinical investigations.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 6;7(49):81621-81633. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13154. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27835595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of serum miR-200a, miR-200b, and miR-200c as candidate biomarkers in epithelial ovarian cancer and their association with clinicopathological features.Clin Transl Oncol. 2015 Oct;17(10):779-87. doi: 10.1007/s12094-015-1303-1. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Clin Transl Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26063644
-
Circulating Cell-Free miR-373, miR-200a, miR-200b and miR-200c in Patients with Epithelial Ovarian Cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;924:3-8. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-42044-8_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27753009
-
miRNAs as prognostic and therapeutic tools in epithelial ovarian cancer.Biomark Med. 2015;9(3):241-57. doi: 10.2217/bmm.14.108. Biomark Med. 2015. PMID: 25731210 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of microRNA in the Prognosis and Diagnosis of Ovarian Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 5;26(7):3413. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073413. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40244333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Helicobacter pylori infection induces abnormal expression of pro-angiogenic gene ANGPT2 and miR-203a in AGS gastric cell line.Braz J Microbiol. 2023 Jun;54(2):791-801. doi: 10.1007/s42770-023-00940-4. Epub 2023 Mar 6. Braz J Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36877445 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA targeting: A novel therapeutic intervention for ovarian cancer.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2023 Jul 24;35:101519. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2023.101519. eCollection 2023 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2023. PMID: 37521375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnosis accuracy of the miR-200 family tumor marker series in ovarian cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Transl Cancer Res. 2022 Jul;11(7):2283-2290. doi: 10.21037/tcr-22-864. Transl Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35966325 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

