Effects of COVID-19 pandemic on mental health of children and adolescents: A systematic review of survey studies
- PMID: 35371484
- PMCID: PMC8972920
- DOI: 10.1177/20503121221086712
Effects of COVID-19 pandemic on mental health of children and adolescents: A systematic review of survey studies
Abstract
Objective: Mental health problems among children and adolescents are increasingly observed during the outbreak of COVID-19, leading to significant healthcare concerns. Survey studies provide unique opportunities for research during this pandemic, while there are no existing systematic reviews in this setting. The objective was to summarize existing survey studies addressing the effects of the current COVID-19 pandemic on the mental health of children and adolescents.
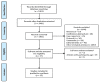
Methods: For this systematic review, we performed an electronic search in multiple databases from December 2019 to December 2020. The quality appraisal of the included studies was performed with the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme Qualitative Checklist. Because of the high methodological heterogeneity between studies, a narrative synthesis of the qualitative data was used.
Results: In total, 35 survey studies with 65,508 participants, ranging from 4 to 19 years of age, are included in this review. Anxiety (28%), depression (23%), loneliness (5%), stress (5%), fear (5%), tension (3%), anger (3%), fatigue (3%), confusion (3%), and worry (3%) were the most common mental health issues reported. Children and adolescents with psychiatric and/or developmental disorders, such as severe obesity, chronic lung disease, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, cystic fibrosis, and obsessive-compulsive disorders, were especially vulnerable to the mental health effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. Age, gender, psychological quality, and negative coping strategies were identified as risk factors for the development of mental health problems. Social and family support, along with a positive coping style, was associated with better outcomes.
Conclusion: The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on mental health of children and adolescents is multifaceted and substantial. Survey studies regarding child and adolescent mental health amid COVID-19 indicated that anxiety, depression, loneliness, stress, and tension are the most observed symptoms. Positive coping strategies with family and social support may be important to achieving better outcomes. Due to limited available evidence, more well-designed studies in this area are urgently needed.
Keywords: COVID-19; Child; adolescent; mental health; review; survey.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Pavone P, Ceccarelli M, Taibi R, et al. Outbreak of COVID-19 infection in children: fear and serenity. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2020; 24(8): 4572–4575. - PubMed
-
- Fegert JM, Vitiello B, Plener PL, et al. Challenges and burden of the Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic for child and adolescent mental health: a narrative review to highlight clinical and research needs in the acute phase and the long return to normality. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health 2020; 14: 20. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical