The rise and spread of the SARS-CoV-2 AY.122 lineage in Russia
- PMID: 35371558
- PMCID: PMC8966696
- DOI: 10.1093/ve/veac017
The rise and spread of the SARS-CoV-2 AY.122 lineage in Russia
Abstract
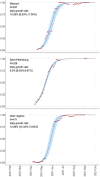
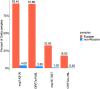
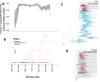
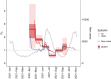
Delta has outcompeted most preexisting variants of SARS-CoV-2, becoming the globally predominant lineage by mid-2021. Its subsequent evolution has led to the emergence of multiple sublineages, most of which are well-mixed between countries. By contrast, here we show that nearly the entire Delta epidemic in Russia has probably descended from a single import event, or from multiple closely timed imports from a single poorly sampled geographic location. Indeed, over 90 per cent of Delta samples in Russia are characterized by the nsp2:K81N + ORF7a:P45L pair of mutations which is rare outside Russia, putting them in the AY.122 sublineage. The AY.122 lineage was frequent in Russia among Delta samples from the start, and has not increased in frequency in other countries where it has been observed, suggesting that its high prevalence in Russia has probably resulted from a random founder effect rather than a transmission advantage. The apartness of the genetic composition of the Delta epidemic in Russia makes Russia somewhat unusual, although not exceptional, among other countries.
Keywords: AY.122; Delta lineage; ORF7a:P45L; SARS-CoV2 in Russia; cross-border transmission of SARS-CoV2; genomic epidemiology of SARS-CoV2.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Update of
-
The rise and spread of the SARS-CoV-2 AY.122 lineage in Russia.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 Dec 5:2021.12.02.21267168. doi: 10.1101/2021.12.02.21267168. medRxiv. 2021. Update in: Virus Evol. 2022 Mar 05;8(1):veac017. doi: 10.1093/ve/veac017. PMID: 34909799 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Auguie B. (2019) Egg: Extensions for “Ggplot2”: Custom Geom, Custom Themes, Plot Alignment, Labelled Panels, Symmetric Scales, and Fixed Panel Size. R package version 0.4.5.
-
- Baty F. et al. (2015) ‘A Toolbox for Nonlinear Regression in R: The Package Nlstools’, Journal of Statistical Software, 66: 51.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

