A Nomogram Based on Molecular Biomarkers and Radiomics to Predict Lymph Node Metastasis in Breast Cancer
- PMID: 35372007
- PMCID: PMC8965370
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.790076
A Nomogram Based on Molecular Biomarkers and Radiomics to Predict Lymph Node Metastasis in Breast Cancer
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to explore the feasibility and efficacy of a non-invasive quantitative imaging evaluation model to assess the lymphatic metastasis of breast cancer based on a radiomics signature constructed using conventional T1-weighted image (T1WI) enhanced MRI and molecular biomarkers.
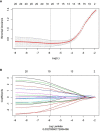
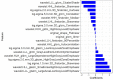
Methods: Patients with breast cancer diagnosed via lymph biopsies between June 2015 and June 2019 were selected for the study. All patients underwent T1WI contrast-enhancement before treatment; lymph biopsy after surgery; and simultaneous Ki-67, COX-2, PR, Her2 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen detection. All images were imported into ITK-SNAP for whole tumor delineation, and AK software was used for radiomics feature extraction. Next, the radiomics signature Rad-score was constructed after reduction of specific radiomic features. A multiple regression logistic model was built by combining the Rad-score and molecular biomarkers based on the minimum AIC.
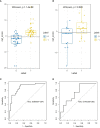
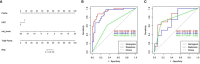
Results: In all, 100 patients were enrolled in this study, including 45 with non-lymph node (LN) metastasis and 55 with LN metastasis. A total of 1,051 texture feature parameters were extracted, and LASSO was used to reduce the dimensionality of the radiomics features. The log(λ) was set to 0.002786, and 19 parameters were retained for the construction of the radiomics tag Rad-score. ROC was used to evaluate the diagnostic efficiency of Rad-score: the area under the ROC curve (AUC) of the Rad-score for identifying non-lymphatic and lymphatic metastases was 0.891 in the training cohort and 0.744 in the validation cohort. With the incorporation of tumor molecular markers, the AUCs of the training cohort and validation cohort of the nomogram were 0.936 and 0.793, respectively, which were notably higher than the AUCs of the clinical parameters in the training and validation cohorts (0.719 and 0.588, respectively).
Conclusion: The combined model constructed using the Rad-score and molecular biomarkers can be used as an effective non-invasive method to assess LN metastasis of breast cancer. Furthermore, it can be used to quantitatively evaluate the risk of breast cancer LN metastasis before surgery.
Keywords: breast cancer; diagnostics; lymph node metastasis; molecular biomarkers; radiomics.
Copyright © 2022 Qiu, Fu, Ye, Wang and Cao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Feasibility of a CT-based lymph node radiomics nomogram in detecting lymph node metastasis in PDAC patients.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 5;12:992906. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.992906. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36276058 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative Prediction of Lymph Node Metastasis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Based on a Radiomics Nomogram of Dual-Parametric MRI Imaging.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 6;12:927077. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.927077. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35875061 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics Based on T2-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Images for Preoperative Evaluation of Lymph Node Metastasis in Rectal Cancer Patients.Front Oncol. 2021 May 10;11:671354. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.671354. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34041033 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting N2 lymph node metastasis in presurgical stage I-II non-small cell lung cancer using multiview radiomics and deep learning method.Med Phys. 2023 Apr;50(4):2049-2060. doi: 10.1002/mp.16177. Epub 2023 Jan 6. Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 36563341 Clinical Trial.
-
Radiomics - Quantitative Biomarker Analysis for Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Prediction: A Review.Curr Med Imaging. 2022;18(1):3-17. doi: 10.2174/1573405617666210303102526. Curr Med Imaging. 2022. PMID: 33655872 Review.
Cited by
-
Predicting Ki-67 expression levels in breast cancer using radiomics-based approaches on digital breast tomosynthesis and ultrasound.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 11;14:1403522. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1403522. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39055558 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of MRI-based radiomic features for EGFR mutation status in non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases: a meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2025 Jan 6;14:1428929. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1428929. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39834943 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a Computed Tomography-based Radiomics Nomogram for Diagnosing Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis in Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas.Adv Radiat Oncol. 2025 Jul 1;10(9):101844. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2025.101844. eCollection 2025 Sep. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40822991 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a radiogenomics model to predict axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer integrating MRI with transcriptome data: A multicohort study.Front Oncol. 2022 Dec 29;12:1076267. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1076267. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36644636 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of an ultrasound-based radiomics nomogram for predicting the luminal from non-luminal type in patients with breast carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 28;12:993466. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.993466. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36530981 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fisher B, Bauer M, Wickerham DL, Redmond CK, Fisher ER, Cruz AB, et al. . Relation of Number of Positive Axillary Nodes to the Prognosis of Patients With Primary Breast Cancer. NSABP Update Cancer (1983) 52:1551–7. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19831101)52:9<1551::aid-cncr2820520902>3.0.co;2-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Say CC, Donegan W. A Biostatistical Evaluation of Complications From Mastectomy. Surg Gynecol Obstet (1974) 138:370–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

