Changes in Gut Microbiota by the Lactobacillus casei Anchoring the K88 Fimbrial Protein Prevented Newborn Piglets From Clinical Diarrhea
- PMID: 35372106
- PMCID: PMC8972131
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.842007
Changes in Gut Microbiota by the Lactobacillus casei Anchoring the K88 Fimbrial Protein Prevented Newborn Piglets From Clinical Diarrhea
Abstract
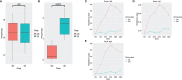
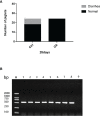
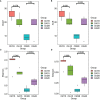
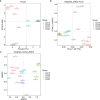
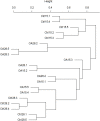
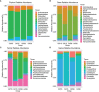
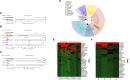
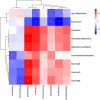
In the last 20 years, accumulating evidence indicates that the gut microbiota contribute to the development, maturation, and regulation of the host immune system and mediate host anti-pathogen defenses. Lactobacillus casei (L.casei) is a normal flora of the gastrointestinal tract in mammals and, as a great mucosal delivery vehicle, has wide use in bioengineering. However, the diarrhea prevention role of commensal intestinal microbiota interfered by the recombinant L.casei (rL.casei) in newborn piglets is not well understood. In our study, newborn piglets orally fed with the rL.casei surface displayed the fimbrial protein K88 of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) and their feces were collected for a period of time after feeding. The next-generation sequencing of these fecal samples showed that the relative abundance of L.casei was significantly increased. The oral administration of rL.casei altered the intestinal microbial community as evidenced by altered microbial diversity and microbial taxonomic composition. Remarkably, the functional enhancing of the intestinal bacterial community by rL.casei was positively correlated with membrane transport, replication, and repair (p < 0.05). The specific antibody detection indicates that high levels of anti-K88 secretory immunoglobulin A (sIgA) were induced in fecal samples and systemic immunoglobulin G was produced in serum. The diarrhea rate in piglets caused by ETEC K88 was decreased by about 24%. Thus, the oral administration of rL.casei not only activated the mucosal and humoral immune responses in vivo but also contributed to shape the intestinal probiotics in newborn piglets and to significantly reduce the diarrhea rates of newborn piglets.
Keywords: 16S rRNA sequencing; ETEC K88; diarrhea; gut microbiota; newborn piglets; rLactobacillus casei.
Copyright © 2022 Qin, Bai, Li, Huang, Li, Wang, Qu, Wang, Yu and Hou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Breiman L. (2001). Random Forests. Mach. Learn 45, 5–32. doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

