Toll-Like Receptor 2 Modulates Pulmonary Inflammation and TNF-α Release Mediated by Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- PMID: 35372108
- PMCID: PMC8968444
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.824027
Toll-Like Receptor 2 Modulates Pulmonary Inflammation and TNF-α Release Mediated by Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the roles that Toll-like receptors (TLRs) play in lung inflammation mediated by Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP).
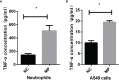
Methods: The changes in TLRs and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) in peripheral blood of children with M. pneumoniae pneumonia (MPP) were monitored, and the interactions of signaling molecules regulating TNF-α release in A549 cells and neutrophils after M. pneumoniae stimulation were investigated. In TLR2 knockout (TLR2-/-) mice, the levels of TNF-α in bronchial alveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and peripheral blood after mycoplasma infection and the pathological changes in the lung tissue of mice were detected.
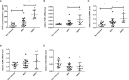
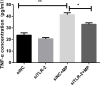
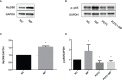
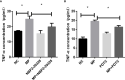
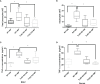
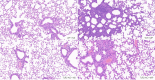
Results: TNF-α levels in peripheral blood of children with MPP were higher than those in non-infected children, and children with refractory MPP had the highest levels of TNF-α and TLR2. TNF-α secretion and TLR2, myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88) and phospho-p65(p-p65) levels were increased in stimulated cells. TNF-α secretion was suppressed upon siRNA-mediated TLR2 silencing. Pharmacological inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and MyD88 effectively reduced TNF-α expression. Compared with wild-type mice, the TNF-α in serum and BALF decreased, and lung pro-inflammatory response was partially suppressed in TLR2-/- mice.
Conclusion: We concluded that TLR2 regulates M. pneumoniae-mediated lung inflammation and TNF-α release through the TLR2-MyD88-NF-κB signaling pathway.
Keywords: A549 cells; MyD88; Mycoplasma pneumoniae; NF-κB; TLR2; TNF-α; neutrophils.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Deng, Zhao, Miao, Gu, Bi, Zhu, Guo, Shi, Xu, Zhao and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

