Phylogeny, Antifungal Susceptibility, and Point Mutations of SQLE Gene in Major Pathogenic Dermatophytes Isolated From Clinical Dermatophytosis
- PMID: 35372131
- PMCID: PMC8972121
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.851769
Phylogeny, Antifungal Susceptibility, and Point Mutations of SQLE Gene in Major Pathogenic Dermatophytes Isolated From Clinical Dermatophytosis
Abstract
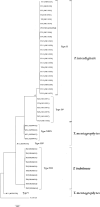
Drug resistance is one of the major challenges to skin fungal infections, especially in tropical and subtropical infections caused by dermatophytes. This study aimed to determine the antifungal susceptibility of clinically dermatophytes and evaluate point mutations in terbinafine-resistant isolates. A total number of 123 clinical dermatophyte isolates in eight species were evaluated in terms of sensitivity to seven major antifungals. Furthermore, the point mutation in squalene epoxidase (SQLE) gene responsible for terbinafine resistance was studied. The dermatophytes species were identified by morphological characteristics and confirmed by the ITS sequencing. Also, the phylogenetic tree was drawn using the RAxML analyses for 123 dermatophytes isolates. A new XXIX genotype was also found in 4 Trichophyton mentagrophytes isolates. Based on the results obtained, terbinafine was the most effective antifungal drug followed by itraconazole and voriconazole. Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton tonsurans were the most susceptible species (MIC50 = 0.01, 0.09 μg/ml), and T. mentagrophytes was the most resistant species (MIC50 = 0.125 μg/ml) to terbinafine. Of the 123 dermatophytes isolates, six isolates showed reduced susceptibility to terbinafine, and only Trichophyton indotineae had a mutation in SQLE gene as a Phe397Leu substitution. Overall, the antifungal susceptibility test is necessary for managing dermatophytosis. These results help physicians to control the course of the disease and provide further insights to select effective drugs for patients with dermatophytosis, especially in tropical and subtropical regions of the world, where dermatophytosis is still a public health problem.
Keywords: Phe397Leu substitution; T. indotineae; antifungal susceptibility testing; dermatophytes; dermatophytosis; point mutation; squalene epoxidase; terbinafine resistance.
Copyright © 2022 Pashootan, Shams-Ghahfarokhi, Chaichi Nusrati, Salehi, Asmar and Razzaghi-Abyaneh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
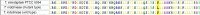
Similar articles
-
Epidemiological trends, antifungal drug susceptibility and SQLE point mutations in etiologic species of human dermatophytosis in Al-Diwaneyah, Iraq.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 3;14(1):12669. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63425-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38830918 Free PMC article.
-
Increased terbinafine resistance among clinical genotypes of Trichophyton mentagrophytes/T. interdigitale species complex harboring squalene epoxidase gene mutations.J Mycol Med. 2024 Sep;34(3):101495. doi: 10.1016/j.mycmed.2024.101495. Epub 2024 Jun 16. J Mycol Med. 2024. PMID: 38896927
-
High terbinafine resistance in Trichophyton interdigitale isolates in Delhi, India harbouring mutations in the squalene epoxidase gene.Mycoses. 2018 Jul;61(7):477-484. doi: 10.1111/myc.12772. Epub 2018 Apr 27. Mycoses. 2018. PMID: 29577447
-
The Emerging Terbinafine-Resistant Trichophyton Epidemic: What Is the Role of Antifungal Susceptibility Testing?Dermatology. 2022;238(1):60-79. doi: 10.1159/000515290. Epub 2021 May 31. Dermatology. 2022. PMID: 34058736 Review.
-
Antifungal resistance in dermatophytes - review of the epidemiology, diagnostic challenges and treatment strategies for managing Trichophyton indotineae infections.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2024 Sep;22(9):739-751. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2024.2390629. Epub 2024 Aug 18. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2024. PMID: 39114868 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Verification of Trichophyton in the Brazilian URM Culture Collection.Mycopathologia. 2024 Jan 13;189(1):2. doi: 10.1007/s11046-023-00811-4. Mycopathologia. 2024. PMID: 38217794
-
Detection of emerging genotypes in Trichophyton mentagrophytes species complex: A proposal for handling biodiversity in dermatophytes.Front Microbiol. 2022 Aug 23;13:960190. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.960190. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36081804 Free PMC article.
-
The emergence and worldwide spread of the species Trichophyton indotineae causing difficult-to-treat dermatophytosis: A new challenge in the management of dermatophytosis.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Sep 29;18(9):e1010795. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010795. eCollection 2022 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 36173977 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
High Prevalence of Terbinafine Resistance Among Trichophyton mentagrophytes/T. interdigitale Species Complex, a Cross-Sectional Study from 2021 to 2022 in Northern Parts of Iran.Mycopathologia. 2024 Jun 12;189(4):52. doi: 10.1007/s11046-024-00855-0. Mycopathologia. 2024. PMID: 38864945
-
Emerging antifungal resistance in Trichophyton mentagrophytes: insights from susceptibility profiling and genetic mutation analysis.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2025 Dec;14(1):2450026. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2025.2450026. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2025. PMID: 39749731 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

