Synthesis and Characterization of Phenylboronic Acid-Modified Insulin With Glucose-Dependent Solubility
- PMID: 35372263
- PMCID: PMC8965884
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2022.859133
Synthesis and Characterization of Phenylboronic Acid-Modified Insulin With Glucose-Dependent Solubility
Abstract
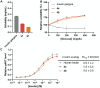
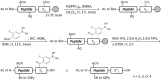
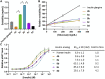
Glucose-responsive insulin represents a promising approach to regulate blood glucose levels. We previously showed that attaching two fluorophenylboronic acid (FPBA) residues to the C-terminal B chain of insulin glargine led to glucose-dependent solubility. Herein, we demonstrated that relocating FPBA from B chain to A chain increased the baseline solubility without affecting its potency. Furthermore, increasing the number of FPBA groups led to increased glucose-dependent solubility.
Keywords: glucose responsiveness; insulin; insulin modification; peptide; phenylboronate.
Copyright © 2022 Lin, Zheng, Purushottam, Zhang and Chou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

