Stearoyl-CoA desaturases sustain cholinergic excitation and copulatory robustness in metabolically aging C. elegans males
- PMID: 35372802
- PMCID: PMC8968053
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104082
Stearoyl-CoA desaturases sustain cholinergic excitation and copulatory robustness in metabolically aging C. elegans males
Abstract
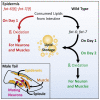
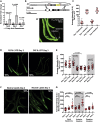
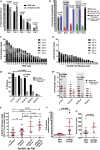
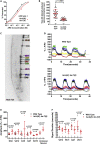
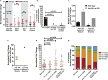
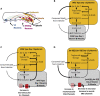
Regulated metabolism is required for behaviors as adults age. To understand how lipid usage affects motor coordination, we studied male Caenorhabditis elegans copulation as a model of energy-intensive behavior. Copulation performance drops after 48 h of adulthood. We found that 12-24 h before behavioral decline, males prioritize exploring and copulation behavior over feeding, suggesting that catabolizing stored metabolites, such as lipids, occurs during this period. Because fat-6/7-encoded stearoyl-CoA desaturases are essential for converting the ingested fatty acids to lipid storage, we examined the copulation behavior and neural calcium transients of fat-6(lf); fat-7(lf) mutants. In wild-type males, intestinal and epithelial fat-6/7 expression increases during the first 48 h of adulthood. The fat-6(lf); fat-7(lf) behavioral and metabolic defects indicate that in aging wild-type males, the increased expression of stearoyl-CoA desaturases in the epidermis may indirectly modulate the levels of EAG-family K+ channels in the reproductive cholinergic neurons and muscles.
Keywords: Behavioral endocrinology; Behavioral neuroscience; Molecular mechanism of behavior.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Alfonso A., Grundahl K., Duerr J.S., Han H.P., Rand J.B. The Caenorhabditis elegans unc-17 gene: a putative vesicular acetylcholine transporter. Science. 1993;261:617–619. - PubMed
-
- Alfonso A., Grundahl K., McManus J.R., Asbury J.M., Rand J.B. Alternative splicing leads to two cholinergic proteins in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Mol. Biol. 1994;241:627–630. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

