Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Nephrotoxicity: Update 2020
- PMID: 35372904
- PMCID: PMC8809100
- DOI: 10.34067/KID.0000852019
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Nephrotoxicity: Update 2020
Abstract
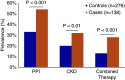
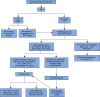
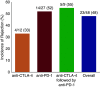
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICPIs) have transformed the landscape of oncology, but are associated with a variety of autoimmune adverse events, including AKI. ICPI-associated AKI (ICPI-AKI) is emerging as an increasingly frequent cause of AKI in patients with cancer, and poses unique diagnostic and management challenges to clinicians who care for these patients. In this review, we describe the incidence and risk factors for ICPI-AKI, including proton pump inhibitor use, CKD, and combination immunotherapy. We discuss the limitations of the various definitions used for ICPI-AKI in prior studies, and propose a novel classification system (definite, probable, and possible ICPI-AKI) that recognizes the diagnostic uncertainty inherent in many cases. We discuss the key clinicopathologic features and treatment strategies for ICPI-AKI, including the role of kidney biopsy versus empirical treatment with steroids. We also explore the under-studied area of ICPI use in the setting of solid organ transplantation, where nephrologists and oncologists must balance the risk of rejection versus treating the underlying malignancy. Finally, we summarize existing data on the role of ICPI rechallenge after an episode of ICPI-AKI.
Keywords: Acute Kidney Injury and ICU Nephrology; Acute kidney injury; Clinical Nephrology; Nephro-Pharmacology; acute interstitial nephritis; acute tubulointerstitial nephritis; immune-related adverse event; immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2020 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
F. Cortazar served as a consultant for ChemoCentryx and Momenta Pharmaceuticals. S. Gupta is a scientific coordinator for the ASCEND trial and reports grants from the National Institutes of Health during the conduct of the study and other from GlaskoSmithKline, outside the submitted work. D. Leaf received grant support from BioPorto Diagnostics. L. Riella had received grant support from Bristol-Meyers-Squib and honorarium from Mallinckrodt.
Figures
References
-
- Leach DR, Krummel MF, Allison JP: Enhancement of antitumor immunity by CTLA-4 blockade. Science 271: 1734–1736, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Callahan MK, Kluger H, Postow MA, Segal NH, Lesokhin A, Atkins MB, Kirkwood JM, Krishnan S, Bhore R, Horak C, Wolchok JD, Sznol M: Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in patients with advanced melanoma: updated survival, response, and safety data in a phase i dose-escalation study. J Clin Oncol, Vol. 36, 2018, pp 391–398 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Weber J, Mandala M, Del Vecchio M, Gogas HJ, Arance AM, Cowey CL, Dalle S, Schenker M, Chiarion-Sileni V, Marquez-Rodas I, Grob JJ, Butler MO, Middleton MR, Maio M, Atkinson V, Queirolo P, Gonzalez R, Kudchadkar RR, Smylie M, Meyer N, Mortier L, Atkins MB, Long GV, Bhatia S, Lebbé C, Rutkowski P, Yokota K, Yamazaki N, Kim TM, de Pril V, Sabater J, Qureshi A, Larkin J, Ascierto PA; CheckMate 238 Collaborators : Adjuvant nivolumab versus ipilimumab in resected stage III or IV melanoma. N Engl J Med 377: 1824–1835, 2017 - PubMed
-
- Garon EB, Rizvi NA, Hui R, Leighl N, Balmanoukian AS, Eder JP, Patnaik A, Aggarwal C, Gubens M, Horn L, Carcereny E, Ahn MJ, Felip E, Lee JS, Hellmann MD, Hamid O, Goldman JW, Soria JC, Dolled-Filhart M, Rutledge RZ, Zhang J, Lunceford JK, Rangwala R, Lubiniecki GM, Roach C, Emancipator K, Gandhi L; KEYNOTE-001 Investigators : Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 372: 2018–2028, 2015 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

