d-Serine Mediates Cellular Proliferation for Kidney Remodeling
- PMID: 35372967
- PMCID: PMC8785787
- DOI: 10.34067/KID.0000832021
d-Serine Mediates Cellular Proliferation for Kidney Remodeling
Abstract
Background: d-serine, a long-term undetected enantiomer of serine, is a biomarker that reflects kidney function and disease activity. The physiologic functions of d-serine are unclear.
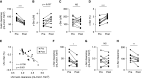
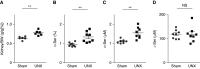
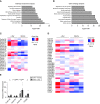
Methods: The dynamics of d-serine were assessed by measuring d-serine in human samples of living kidney donors using two-dimensional high-performance liquid chromatography, and by autoradiographic studies in mice. The effects of d-serine on the kidney were examined by gene expression profiling and metabolic studies using unilateral nephrectomy mice, and genetically modified cells.
Results: Unilateral nephrectomy in human living kidney donors decreases urinary excretion and thus increases the blood level of d-serine. d-serine is quickly and dominantly distributed to the kidney on injection in mice, suggesting the kidney is a main target organ. Treatment of d-serine at a low dose promotes the enlargement of remnant kidney in mouse model. Mechanistically, d-serine activates the cell cycle for tissue remodeling through an mTOR-related pathway.
Conclusions: d-serine is a physiologic molecule that promotes kidney remodeling. Besides its function as a biomarker, d-serine has a physiologic activity that influences kidney function.
Keywords: basic science; biomarker; cell cycle; chronic kidney disease; d-serine; glomerular filtration rate; kidney remodeling; kidney transplantation; mTOR; physiological activity; renal-physiology; urinary excretion.
Copyright © 2021 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
A. Hesaka reports having an ownership interest in KAGAMI Inc. M. Mita and M. Nakane are co-founders of KAGAMI Inc., a startup company working on chiral amino acids analysis and research for medical application. T. Kimura reports having an ownership interest in KAGAMI Inc.; reports receiving research funding from Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd., Shiseido Co., Ltd, and KAGAMI Inc. T. Kimura and M. Mita are preparing patent application which is related with this work. Y. Isaka reports receiving research funding from Bayel Yakuhin Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Kissei Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Kyowa Kirin Co. Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., and Teijin Ltd.; and reports speakers bureau from Bayel Yakuhin Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Kissei Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Kyowa Kirin Co. Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., and Teijin Ltd. All remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures


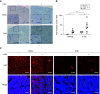
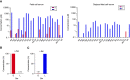
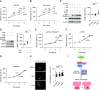
References
-
- Nagata Y, Akino T, Ohno K, Kataoka Y, Ueda T, Sakurai T, Shiroshita K, Yasuda T: Free D-amino acids in human plasma in relation to senescence and renal diseases. Clin Sci (Lond) 73: 105–108, 1987. - PubMed
-
- International Society of Nephrology : The under-recognized epidemic: Worldwide, over 850 million people suffer from kidney diseases. 2018. Available at: https://archive.theisn.org/images/ASN_PR_20180627_Final6.26.18Press_E.pdf. Accessed October 1, 2018
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

