A Propensity Score-Matched Observational Study of Remdesivir in Patients with COVID-19 and Severe Kidney Disease
- PMID: 35373125
- PMCID: PMC8967642
- DOI: 10.34067/KID.0006152021
A Propensity Score-Matched Observational Study of Remdesivir in Patients with COVID-19 and Severe Kidney Disease
Abstract
Background: Remdesivir is not currently approved for patients with eGFR <30 ml/min per 1.73 m2. We aimed to determine the safety of remdesivir in patients with kidney failure.
Methods: This study was a retrospective cohort study of patients with COVID-19 hospitalized between May 2020 and January 2021 with eGFR <30 ml/min per 1.73 m2 who received remdesivir and historical controls with COVID-19 hospitalized between March 1, 2020 and April 30, 2020 prior to the emergency use authorization of remdesivir within a large health care system. Patients were 1:1 matched by propensity scores accounting for factors associated with treatment assignment. Adverse events and hospital outcomes were recorded by manual chart review.
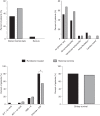
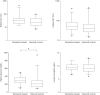
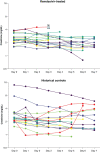
Results: The overall cohort included 34 hospitalized patients who initiated remdesivir within 72 hours of hospital admission with eGFR<30 ml/min per 1.73 m2 and 217 COVID-19 controls with eGFR <30 ml/min per 1.73 m2. The propensity score-matched cohort included 31 remdesivir-treated patients and 31 nonremdesivir-treated controls. The mean age was 74.0 (SD=13.8) years, 57% were women, and 68% were white participants. A total of 26% had ESKD. Among patients who were not on dialysis prior to initiating remdesivir, one developed worsening kidney function (defined as ≥50% increase in creatinine or initiation of KRT) compared with three in the historical control group. There was no increased risk of cardiac arrythmia, cardiac arrest, altered mental status, or clinically significant anemia or liver function test abnormalities. There was a significantly increased risk of hyperglycemia, which may be partly explained by the increased use of dexamethasone in the remdesivir-treated population.
Conclusions: In this propensity score-matched study, remdesivir was well tolerated in patients with eGFR <30 ml/min per 1.73 m2.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; acute kidney injury; antiviral; chronic kidney disease; dialysis; propensity score; remdesivir.
Copyright © 2022 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
M.E. Sise reports consultancy agreements with Bioporto; research funding from Abbvie, EMD-Serono, Gilead Sciences, and Merck; honoraria from the International Society of Hemodialysis for the Hemodialysis University Lecture; and scientific advisor or membership with Gilead Sciences as a scientific advisory board member and Travere Therapeutics as an scientific advisory board member. All remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Johns Hopkins University of Medicine Coronavirus Resource Center : COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU), 2021. Available at: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html. Accessed August 10, 2021
-
- Puelles VG, Lütgehetmann M, Lindenmeyer MT, Sperhake JP, Wong MN, Allweiss L, Chilla S, Heinemann A, Wanner N, Liu S, Braun F, Lu S, Pfefferle S, Schröder AS, Edler C, Gross O, Glatzel M, Wichmann D, Wiech T, Kluge S, Pueschel K, Aepfelbacher M, Huber TB: Multiorgan and renal tropism of SARS-CoV-2. N Engl J Med 383: 590–592, 2020. 10.1056/NEJMc2011400 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hirsch JS, Ng JH, Ross DW, Sharma P, Shah HH, Barnett RL, Hazzan AD, Fishbane S, Jhaveri KDNorthwell COVID-19 Research ConsortiumNorthwell Nephrology COVID-19 Research Consortium : Acute kidney injury in patients hospitalized with COVID-19. Kidney Int 98: 209–218, 2020. 10.1016/j.kint.2020.05.006 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Richardson S, Hirsch JS, Narasimhan M, Crawford JM, McGinn T, Davidson KW, Barnaby DP, Becker LB, Chelico JD, Cohen SL, Cookingham J, Coppa K, Diefenbach MA, Dominello AJ, Duer-Hefele J, Falzon L, Gitlin J, Hajizadeh N, Harvin TG, Hirschwerk DA, Kim EJ, Kozel ZM, Marrast LM, Mogavero JN, Osorio GA, Qiu M, Zanos TP; the Northwell COVID-19 Research Consortium : Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area. JAMA 323: 2052–2059, 2020. 10.1001/jama.2020.6775 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

