COVID-19 in Patients with Glomerular Disease: Follow-Up Results from the IRoc-GN International Registry
- PMID: 35373130
- PMCID: PMC8967646
- DOI: 10.34067/KID.0006612021
COVID-19 in Patients with Glomerular Disease: Follow-Up Results from the IRoc-GN International Registry
Abstract
Background: The acute and long-term effects of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection in individuals with GN are still unclear. To address this relevant issue, we created the International Registry of COVID-19 infection in GN.
Methods: We collected serial information on kidney-related and -unrelated outcomes from 125 GN patients (63 hospitalized and 62 outpatients) and 83 non-GN hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and a median follow-up period of 6.4 (interquartile range 2.3-9.6) months after diagnosis. We used logistic regression for the analyses of clinical outcomes and linear mixed models for the longitudinal analyses of eGFR. All multiple regression models were adjusted for age, sex, ethnicity, and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitor use.
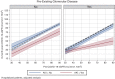
Results: After adjustment for pre-COVID-19 eGFR and other confounders, mortality and AKI did not differ between GN patients and controls (adjusted odds ratio for AKI=1.28; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.46 to 3.60; P=0.64). The main predictor of AKI was pre-COVID-19 eGFR (adjusted odds ratio per 1 SD unit decrease in eGFR=3.04; 95% CI, 1.76 to 5.28; P<0.001). GN patients developing AKI were less likely to recover pre-COVID-19 eGFR compared with controls (adjusted 6-month post-COVID-19 eGFR=0.41; 95% CI, 0.25 to 0.56; times pre-COVID-19 eGFR). Shorter duration of GN diagnosis, higher pre-COVID-19 proteinuria, and diagnosis of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis or minimal change disease were associated with a lower post-COVID-19 eGFR.
Conclusions: Pre-COVID-19 eGFR is the main risk factor for AKI regardless of GN diagnosis. However, GN patients are at higher risk of impaired eGFR recovery after COVID-19-associated AKI. These patients (especially those with high baseline proteinuria or a diagnosis of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis or minimal change disease) should be closely monitored not only during the acute phases of COVID-19 but also after its resolution.
Keywords: COVID-19; follow-up studies; glomerular and tubulointerstitial diseases; glomerular disease; kidney glomerulus; registries.
Copyright © 2022 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
O. Bestard reports patents and inventions with Oxford Immunotec and is associate editor of Transplant International and Frontiers in Immunology. A. Bruchfeld reports consultancy agreements with AstraZeneca, Chemocentryx, Fresenius, and Merck; a research grant from AstraZeneca; honoraria from Bayer, Chemocentryx, Fresenius, Merck, and Vifor; and is a member of the ERA-EDTA scientific advisory board 2018–2024, chair of the ERA-EDTA Immunonephrology Working Group, and vice-chair of the Swedish Renal Fund. G. Comai reports honoraria from Alexion, Astellas, and Novartis. P. Cravedi reports honoraria as an advisor for Chinook Therapeutics and is associate editor for the Journal of Nephrology and the American Journal of Transplantation. G. Fernandez Juarez reports research funding from Instituto Salud Calos III and honoraria from Alexion and GSK. E. Fiaccadori is on the editorial board of the Journal of Nephrology and Blood Purification and is a member of the Italian Society of Nephrology and the European Society of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. O. Flossmann reports consultancy agreements with Vifor Pharma has other interests/relationships with the British Medical Association, European Vasculitis Society, Renal Association (UK), Royal College of Physicians London, and UK Ireland Vasculitis Society. C. García-Carro reports consultancy agreements with Astellas, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim Lilly, Esteve, Novartis and Baxter, Novo Nordisk, and Otsuka; honoraria from Astellas, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim Lilly, Esteve, Novartis and Baxter, Novo Nordisk, and Otsuka; and is a scientific advisor for or member of AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim Lilly, Mundipharma, and Novo Nordisk. M. Griffith reports honoraria from Retrophin’s advisory board. A. J. Hamilton is on the editorial board of the Journal of Kidney Care and is a member of the SONG-Kids Life Participation Expert Working Group. T. Leach reports honoraria from Janssen for conference attendance in 2012 and is a scientific advisor to the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. L. Lightstone reports consultancy agreements with Achillion, Alexion, AstraZeneca, Aurinia, BMS, GSK, Kezar, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche; honoraria from Alexion, AstraZeneca, BMS, GSK, and Pfizer; is a scientific advisor or member of EU Exec Lupus Nephritis Trials Network; is on the advisory board of Nature Reviews Nephrology; participates in a speakers’ bureau for Alexion and GSK; is a trustee of Kidney Research UK 2018–2022; is an executive member of the International Society of Nephrology 2021–2023; is deputy chair of Western Regional Board of the International Society of Nephrology; and is a clinical expert representing the Renal Association response to NICE on STA for belimumab in lupus 2020–2021. U. Maggiore reports consultancy agreements with Biotest, Chiesi, GSK, Hansa, Novartis, Sandoz, and Takeda. J. Manrique is a scientific advisor for or member of AstraZeneca, Boehringer, and Viphor Pharma. E. Morales reports consultancy agreements with Alexion, Celgene, Viphor Fresenius, and Vifor Pharma. J.A. Niño-Cruz reports research funding from Pfizer Scientific Institute and participates in a speakers’ bureau for Takeda and Roche. A. Ortiz reports consultancy agreements with Retrophin and Sanofi Genzyme; research funding from AstraZeneca, Mundipharma, and Sanofi Genzyme; honoraria from Advicciene, Alexion, Amgen, Amicus, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Chiesi, Fresenius Medical Care, Idorsia, Kyowa Kirin, Menarini, Otsuka, Sanofi Genzyme, and Vifor Fresenius Medical Care Renal Pharma; is a member of the Spanish Society of Nephrology; is editor-in-chief of the Clinical Kidney Journal; is on the editorial boards of the Journal of Nephrology, Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, and Peritoneal Dialysis International; is a member of SOMANE and ERA Councils; is on the board of directors for IIS-Fundacion Jimenez Diaz UAM; is on the scientific advisory board of the Dutch Kidney Foundation; honoraria listed above are for speaker engagements: Advicciene, Alexion, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Amicus, Amgen, Bayer, Chiesi, Fresenius Medical Care, Idorsia, Kyowa Kirin, Menarini, Otsuka, Sanofi Genzyme, and Vifor Fresenius Medical Care Renal Pharma. S. Sinha reports consultancy agreements with Sanifit; research funding from Amgen, AstraZeneca, and Ethicon; and honoraria from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Napp Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, and Sanofi Genzyme. M.F. Slon-Roblero reports consultancy agreements with Baxter, Fresenius, and Nipro; and honoraria from Baxter, Fresenius, and Nipro. M.J. Soler reports consultancy agreements with AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer, Esteve, Jansen, Mundipharma, Novo Nordisk, Travere, and ICU; research funding from Abbvie and Boehringer; honoraria from AstraZeneca, Boehringer, Esteve, FMC, Jansen, ICU Medical, Mundipharma, Novo Nordisk, Otsuka, and Travere; patents and inventions: U691ES00; is a scientific advisor for or member of BMC Nephrology and Clinical Kidney Journal; is a former member of ERA-EDTA Council; participates in a speakers’ bureau for AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer, Esteve, FMC, Jansen, Mundipharma, Novo Nordisk, and Vifor; is a member of the Sociedad Española de Nefrología and Sociedad Catalana de Nefrologia; and is elected editor-in-chief of the Clinical Kidney Journal. All remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Waldman M, Soler MJ, García-Carro C, Lightstone L, Turner-Stokes T, Griffith M, Torras J, Valenzuela LM, Bestard O, Geddes C, Flossmann O, Budge KL, Cantarelli C, Fiaccadori E, Delsante M, Morales E, Gutierrez E, Niño-Cruz JA, Martinez-Rueda AJ, Comai G, Bini C, La Manna G, Slon MF, Manrique J, Agraz I, Sinaii N, Cravedi P: Results from the IRoc-GN international registry of patients with COVID-19 and glomerular disease suggest close monitoring. Kidney Int 99: 227–237, 2021. 10.1016/j.kint.2020.10.032 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Harris PA, Taylor R, Minor BL, Elliott V, Fernandez M, O’Neal L, McLeod L, Delacqua G, Delacqua F, Kirby J, Duda SN; REDCap Consortium : The REDCap consortium: Building an international community of software platform partners. J Biomed Inform 95: 103208, 2019. 10.1016/j.jbi.2019.103208 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fu EL, Janse RJ, de Jong Y, van der Endt VHW, Milders J, van der Willik EM, de Rooij ENM, Dekkers OM, Rotmans JI, van Diepen M: Acute kidney injury and kidney replacement therapy in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Kidney J 13: 550–563, 2020. 10.1093/ckj/sfaa160 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chan L, Chaudhary K, Saha A, Chauhan K, Vaid A, Zhao S, Paranjpe I, Somani S, Richter F, Miotto R, Lala A, Kia A, Timsina P, Li L, Freeman R, Chen R, Narula J, Just AC, Horowitz C, Fayad Z, Cordon-Cardo C, Schadt E, Levin MA, Reich DL, Fuster V, Murphy B, He JC, Charney AW, Böttinger EP, Glicksberg BS, Coca SG, Nadkarni GN; Mount Sinai COVID Informatics Center (MSCIC) : AKI in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. J Am Soc Nephrol 32: 151–160, 2021. 10.1681/ASN.2020050615 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ng JH, Hirsch JS, Hazzan A, Wanchoo R, Shah HH, Malieckal DA, Ross DW, Sharma P, Sakhiya V, Fishbane S, Jhaveri KD; Northwell Nephrology COVID-19 Research Consortium : Outcomes among patients hospitalized with COVID-19 and acute kidney injury. Am J Kidney Dis 77: 204–215.e1, 2021. 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.09.002 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

