Hsa_circ_0060927 participates in the regulation of Caudatin on colorectal cancer malignant progression by sponging miR-421/miR-195-5p
- PMID: 35373390
- PMCID: PMC9102760
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.24393
Hsa_circ_0060927 participates in the regulation of Caudatin on colorectal cancer malignant progression by sponging miR-421/miR-195-5p
Abstract
Background: Caudatin is extracted from radix cynanchi bungei and has an inhibitory effect on cancer progression. The study aims to reveal the impacts of hsa_circ_0060927 on Caudatin-mediated colorectal cancer (CRC) development and the underneath mechanism.
Methods: The expression levels of hsa_circ_0060927, microRNA-421 (miR-421) and miR-195-5p were detected by quantitative real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. The protein expression was analyzed by Western blot or immunohistochemistry assay. Cell viability and proliferation were analyzed by 3-(4,5)-dimethylthiahiazo (-z-y1)-3,5-di-phenytetrazoliumromide or 5-Ethynyl-29-deoxyuridine assay. Cell apoptosis was quantified by flow cytometry analysis. Cell migration and invasion were investigated by transwell assay. The putative associations among hsa_circ_0060927, miR-421 and miR-195-5p were predicted by the starbase online database, and identified by dual-luciferase reporter, RNA pull-down and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assays. The impacts of Caudatin treatment on tumor growth in vivo were revealed by a xenograft tumor model assay.
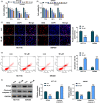
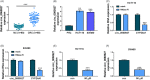
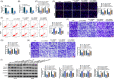
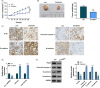
Results: Hsa_circ_0060927 expression was significantly upregulated, whereas miR-421 and miR-195-5p were downregulated in CRC tissues and cells compared with control groups. Hsa_circ_0060927 expression was closely associated with lymph node metastasis and tumor-node-metastasis stage. Caudatin treatment significantly decreased hsa_circ_0060927 expression but increased miR-421 and miR-195-5p expression. Caudatin exposure suppressed CRC cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and induced cell apoptosis; however, hsa_circ_0060927 overexpression hindered these impacts. Additionally, hsa_circ_0060927 was associated with miR-421/miR-195-5p. Depletion of miR-421 or miR-195-5p attenuated the influences of hsa_circ_0060927 silencing on CRC development. Furthermore, Caudatin treatment repressed tumor growth in vivo.
Conclusion: Caudatin inhibited CRC cell malignancy through the hsa_circ_0060927/miR-421/miR-195-5p pathway, which provided a potential therapeutic agent for CRC.
Keywords: Caudatin; colorectal cancer; hsa_circ_0060927; miR-195-5p; miR-421.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Global Burden of Disease Cancer C , Fitzmaurice C, Allen C, et al. Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability‐adjusted life‐years for 32 cancer groups, 1990 to 2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3(4):524‐548. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brody H. Colorectal cancer. Nature. 2015;521(7551):S1. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

