DOC2b Enhances β-Cell Function via a Novel Tyrosine Phosphorylation-Dependent Mechanism
- PMID: 35377441
- PMCID: PMC9163558
- DOI: 10.2337/db21-0681
DOC2b Enhances β-Cell Function via a Novel Tyrosine Phosphorylation-Dependent Mechanism
Abstract
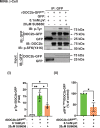
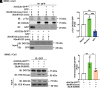
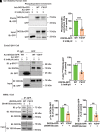
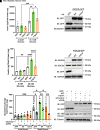
Double C2 domain Β (DOC2b) protein is required for glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) in β-cells, the underlying mechanism of which remains unresolved. Our biochemical analysis using primary human islets and human and rodent clonal β-cells revealed that DOC2b is tyrosine phosphorylated within 2 min of glucose stimulation, and Src family kinase member YES is required for this process. Biochemical and functional analysis using DOC2bY301 mutants revealed the requirement of Y301 phosphorylation for the interaction of DOC2b with YES kinase and increased content of VAMP2, a protein on insulin secretory granules, at the plasma membrane (PM), concomitant with DOC2b-mediated enhancement of GSIS in β-cells. Coimmunoprecipitation studies demonstrated an increased association of DOC2b with ERM family proteins in β-cells following glucose stimulation or pervanadate treatment. Y301 phosphorylation-competent DOC2b was required to increase ERM protein activation, and ERM protein knockdown impaired DOC2b-mediated boosting of GSIS, suggesting that tyrosine-phosphorylated DOC2b regulates GSIS via ERM-mediated granule localization to the PM. Taken together, these results demonstrate the glucose-induced posttranslational modification of DOC2b in β-cells, pinpointing the kinase, site of action, and downstream signaling events and revealing a regulatory role of YES kinase at various steps in GSIS. This work will enhance the development of novel therapeutic strategies to restore glucose homeostasis in diabetes.
© 2022 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures



References
-
- Ashcroft FM, Harrison DE, Ashcroft SJ. Glucose induces closure of single potassium channels in isolated rat pancreatic beta-cells. Nature 1984;312:446–448 - PubMed
-
- Daniel S, Noda M, Straub SG, Sharp GW. Identification of the docked granule pool responsible for the first phase of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Diabetes 1999;48:1686–1690 - PubMed
-
- Rorsman P, Ashcroft FM, Trube G. Single Ca channel currents in mouse pancreatic B-cells. Pflugers Arch 1988;412:597–603 - PubMed
-
- Satin LS, Cook DL. Voltage-gated Ca2+ current in pancreatic B-cells. Pflugers Arch 1985;404:385–387 - PubMed
-
- Rorsman P, Braun M. Regulation of insulin secretion in human pancreatic islets. Annu Rev Physiol 2013;75:155–179 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

