Effects of JZTX-V on the wild type Kv4.3 Expressed in HEK293T and Molecular Determinants in the Voltage-sensing Domains of Kv4.3 Interacting with JZTX-V
- PMID: 35378047
- PMCID: PMC8986175
- DOI: 10.1080/19336950.2022.2053420
Effects of JZTX-V on the wild type Kv4.3 Expressed in HEK293T and Molecular Determinants in the Voltage-sensing Domains of Kv4.3 Interacting with JZTX-V
Abstract
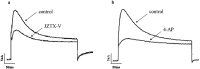
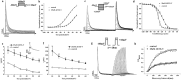
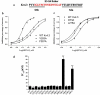
JZTX-V is a toxin isolated from the venom of the Chinese spider Chilobrachys jingzhao. Previous studies had shown that JZTX-V could inhibit the transient outward potassium current of Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 expressed in Xenopus oocytes but had no effects on Kv1.2-1.4. However, the underlying action mechanism of JZTX-V on Kv4.3 remains unclear. In our study, JZTX-V could inhibit not only transient outward potassium currents evoked in small-sized DRG neurons but also Kv4.3-encoded currents expressed in HEK293T cells in the concentration and voltage dependence. The half maximal inhibitory concentration of JZTX-V on Kv4.3 was 9.6 ± 1.2 nM. In addition, the time course for JZTX-V inhibition and release of inhibition after washout were 15.8 ± 1.54 s and 58.8 ± 4.35 s. Electrophysiological assays indicated that 25 nM JZTX-V could shift significantly the voltage dependence of steady-state activation and steady-state inactivation to depolarization. Meanwhile, 25 nM JZTX-V decreased markedly the time constant of activation and inactivation but had no effect on the time constant of recovery from inactivation. To study the molecular determinants of Kv4.3, we performed alanine scanning on a conserved motif of Kv4.3 and assayed the affinity between mutants and JZTX-V. The results not only showed that I273, L275, V283, and F287 were molecular determinants in the conserved motif of Kv4.3 for interacting with JZTX-V but also speculated the underlying action mechanism that the hydrophobic interaction and steric effects played key roles in the binding of JZTX-V with Kv4.3. In summary, our studies have laid a scientific theoretical foundation for further research on the interaction mechanism between JZTX-V and Kv4.3.
Keywords: JZTX-V; electrophysiological assays; kv4.3; molecular determinants; mutants.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures



References
-
- González C, Baez-Nieto D, Valencia I, et al. K (+) channels: function-structural overview. Compr Physiol. 2012;2:2087–2149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
