Age-Independent Preoperative Chemosensitivity and 5-Year Outcome Determined by Combined 70- and 80-Gene Signature in a Prospective Trial in Early-Stage Breast Cancer
- PMID: 35378634
- PMCID: PMC9174138
- DOI: 10.1245/s10434-022-11666-2
Age-Independent Preoperative Chemosensitivity and 5-Year Outcome Determined by Combined 70- and 80-Gene Signature in a Prospective Trial in Early-Stage Breast Cancer
Abstract
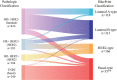
Background: The Neoadjuvant Breast Symphony Trial (NBRST) demonstrated the 70-gene risk of distant recurrence signature, MammaPrint, and the 80-gene molecular subtyping signature, BluePrint, precisely determined preoperative pathological complete response (pCR) in breast cancer patients. We report 5-year follow-up results in addition to an exploratory analysis by age and menopausal status.
Methods: The observational, prospective NBRST (NCT01479101) included 954 early-stage breast cancer patients aged 18-90 years who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy and had clinical and genomic data available. Chemosensitivity and 5-year distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS) and overall survival (OS) were assessed. In a post hoc subanalysis, results were stratified by age (≤ 50 vs. > 50 years) and menopausal status in patients with hormone receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative (HR+/HER2-) tumors.
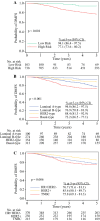
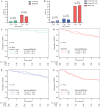
Results: MammaPrint and BluePrint further classified 23% of tumors to a different subtype compared with immunohistochemistry, with more precise correspondence to pCR rates. Five-year DMFS and OS were highest in MammaPrint Low Risk, Luminal A-type and HER2-type tumors, and lowest in MammaPrint High Risk, Luminal B-type and Basal-type tumors. There was no significant difference in chemosensitivity between younger and older patients with Low-Risk (2.2% vs. 3.8%; p = 0.64) or High-Risk tumors (14.5% vs. 11.5%; p = 0.42), or within each BluePrint subtype; this was similar when stratifying by menopausal status. The 5-year outcomes were comparable by age or menopausal status for each molecular subtype.
Conclusion: Intrinsic preoperative chemosensitivity and long-term outcomes were precisely determined by BluePrint and MammaPrint regardless of patient age, supporting the utility of these assays to inform treatment and surgical decisions in early-stage breast cancer.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

