This is a preprint.
Spatial-CITE-seq: spatially resolved high-plex protein and whole transcriptome co-mapping
- PMID: 35378748
- PMCID: PMC8978952
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-1499315/v1
Spatial-CITE-seq: spatially resolved high-plex protein and whole transcriptome co-mapping
Update in
-
High-plex protein and whole transcriptome co-mapping at cellular resolution with spatial CITE-seq.Nat Biotechnol. 2023 Oct;41(10):1405-1409. doi: 10.1038/s41587-023-01676-0. Epub 2023 Feb 23. Nat Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36823353 Free PMC article.
Abstract
We present spatial-CITE-seq for high-plex protein and whole transcriptome co-mapping, which was firstly demonstrated for profiling 198 proteins and transcriptome in multiple mouse tissue types. It was then applied to human tissues to measure 283 proteins and transcriptome that revealed spatially distinct germinal center reaction in tonsil and early immune activation in skin at the COVID-19 mRNA vaccine injection site. Spatial-CITE-seq may find a range of applications in biomedical research.
Figures
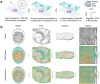
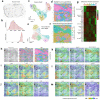
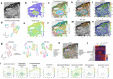
References
-
- Stahl P.L. et al. Visualization and analysis of gene expression in tissue sections by spatial transcriptomics. Science 353, 78–82 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Burgess D.J. Spatial transcriptomics coming of age. Nat Rev Genet 20, 317 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Larsson L., Frisen J. & Lundeberg J. Spatially resolved transcriptomics adds a new dimension to genomics. Nat Methods 18, 15–18 (2021). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

