Decongestive progressive resistance exercise with an adjustable compression wrap for breast cancer-related lymphoedema (DREAM): protocol for a randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 35379618
- PMCID: PMC8981291
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-053165
Decongestive progressive resistance exercise with an adjustable compression wrap for breast cancer-related lymphoedema (DREAM): protocol for a randomised controlled trial
Abstract
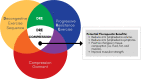
Introduction: Breast cancer-related lymphoedema (BCRL) is a chronic swelling in the arm on the side of the breast cancer surgery, affecting one in five women. Recent studies in BCRL have demonstrated that resistance exercise can improve symptoms and quality of life without worsening lymphoedema. No studies have explored whether combining the principles of progressive resistance exercise training with therapeutic strategies of compression therapy and the decongestive lymphatic exercise sequence are beneficial in reducing arm lymphoedema volume. The aim of this three-arm, provincial randomised controlled trial is to determine the efficacy of a 12-week decongestive progressive resistance exercise (DRE) programme in combination with the one of two types of compression garments compared with standard care.
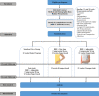
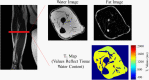
Methods and analysis: Sixty women with BCRL will be recruited and randomly assigned to one of the following three groups: (1) Standard care, (2) DRE with use of a daytime compression garment during exercise and (3) DRE with use of an adjustable compression wrap during exercise. The primary outcome is the percentage reduction in arm lymphoedema volume. Secondary outcomes include bioimpedance analysis, muscular strength, shoulder range of motion, physical activity level and health-related quality of life. Exploratory outcomes include evaluating changes in arm tissue composition using MRI and examining outcomes between the two DRE experimental groups. The primary analysis will compare changes between the groups from baseline to week 12 reflecting the end of the randomised control trial period.
Ethics and dissemination: The trial has received ethics approval from the Health Research Ethics Board of Alberta: Cancer Committee. The study results will be disseminated through scientific peer-reviewed publications, and presented at national and international conferences, and other media portals. The programme protocol will be shared with healthcare professionals and patient groups through clinical workshops and webinars.
Trial registration number: NCT05022823.
Protocol version: 12 November 2021.
Issue date: 26 April 2021.
Keywords: Adult oncology; Breast tumours; COMPLEMENTARY MEDICINE; Rehabilitation medicine.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Addition of prophylactic compression garments to standard care to prevent irreversible lower limb lymphoedema after gynaeco-oncological therapy (Gynolymph): protocol for a randomised controlled trial embedded within an observation cohort study.BMJ Open. 2024 Nov 1;14(10):e088851. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-088851. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 39486824 Free PMC article.
-
Manual lymphatic drainage with or without fluoroscopy guidance did not substantially improve the effect of decongestive lymphatic therapy in people with breast cancer-related lymphoedema (EFforT-BCRL trial): a multicentre randomised trial.J Physiother. 2022 Apr;68(2):110-122. doi: 10.1016/j.jphys.2022.03.010. Epub 2022 Apr 12. J Physiother. 2022. PMID: 35428594 Clinical Trial.
-
Protocol of a randomised controlled trial regarding the effectiveness of fluoroscopy-guided manual lymph drainage for the treatment of breast cancer-related lymphoedema (EFforT-BCRL trial).Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2018 Feb;221:177-188. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2017.12.023. Epub 2017 Dec 16. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2018. PMID: 29277358 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of acupuncture on breast cancer-related lymphoedema: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.Acupunct Med. 2019 Feb;37(1):16-24. doi: 10.1136/acupmed-2018-011668. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Acupunct Med. 2019. PMID: 30845813
-
Effects of photobiomodualtion therapy on breast cancer-related lymphoedema: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.Complement Ther Med. 2019 Dec;47:102200. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2019.102200. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Complement Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31780036
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
