Current clinical practice and outcome of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for early breast cancer: analysis of individual data from 94,638 patients treated in 55 breast cancer centers
- PMID: 35380257
- PMCID: PMC9984341
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-022-03938-x
Current clinical practice and outcome of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for early breast cancer: analysis of individual data from 94,638 patients treated in 55 breast cancer centers
Abstract
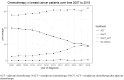
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) is frequently used in patients with early breast cancer. Randomized controlled trials have demonstrated similar survival after NACT or adjuvant chemotherapy (ACT). However, certain subtypes may benefit more when NACT contains regimes leading to high rates of pathologic complete response (pCR) rates. In this study we analyzed data using the OncoBox research from 94,638 patients treated in 55 breast cancer centers to describe the current clinical practice of and outcomes after NACT under routine conditions. These data were compared to patients treated with ACT. 40% of all patients received chemotherapy. The use of NACT increased over time from 5% in 2007 up to 17.3% in 2016. The proportion of patients receiving NACT varied by subtype. It was low in patients with HR-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer (5.8%). However, 31.8% of patients with triple-negative, 31.9% with HR-negative/HER2-positive, and 26.5% with HR-positive/HER2-positive breast cancer received NACT. The rates of pCR were higher in patients with HR-positive/HER2-positive, HR-negative/HER2-positive and triple-negative tumors (36, 53 and 38%) compared to HR-positive/HER2-negative tumors (12%). PCR was achieved more often in HER2-positive and triple-negative tumors over time.This is the largest study on use and effects of NACT in German breast cancer centers. It demonstrates the increased use of NACT based on recommendations in current clinical guidelines. An improvement of pCR was shown in particular in HER2-positive and triple-negative breast cancer, which is consistent with data from randomized controlled trails.
Keywords: Breast cancer centers; Early breast cancer; Guidelines; Neoadjuvant chemotherapy; Oncobox research.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests related to the study.
Figures
References
-
- Caudle AS, Yang WT, Krishnamurthy S et al (2016) Improved axillary evaluation following neoadjuvant therapy for patients with node-positive breast cancer using selective evaluation of clipped nodes: implementation of targeted axillary dissection. JCO 34:1072–1078. 10.1200/JCO.2015.64.0094 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cortazar P, Zhang L, Untch M et al (2014) Pathological complete response and long-term clinical benefit in breast cancer: the CTNeoBC pooled analysis. Lancet 384:164–172. 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62422-8 - PubMed
-
- German Cancer Society, German Society for Senology (2020) Annual Report 2020 of the Certified Breast Cancer Centres (BCCs). Audit year2019/ indicator year 2018. Berlin
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous