[Complex pelvic trauma : A case report with special consideration of the accompanying urogenital injury]
- PMID: 35380265
- PMCID: PMC9842583
- DOI: 10.1007/s00113-022-01170-3
[Complex pelvic trauma : A case report with special consideration of the accompanying urogenital injury]
Abstract
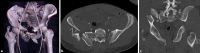
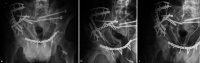
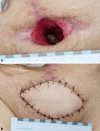
The following case report shows a young male patient with a complex pelvic trauma due to a traffic accident. In addition to the pelvic ring fracture, he also suffered a severe accompanying injury to the efferent urinary tract in combination with extensive damage of the lumbosacral plexus. Multiple extensive operations were necessary to address the C3 fracture of the pelvic ring and the bladder injury. Due to an infection a wound healing disorder subsequently occurred, which necessitated a myocutaneous flap plasty. This case highlights the complexity of this injury and confirms the necessity for an interdisciplinary individualized treatment.
Die folgende Kasuistik zeigt einen jungen Mann, der sich im Rahmen eines Verkehrsunfalles ein komplexes Beckentrauma mit schwerer Begleitverletzung der ableitenden Harnwege sowie ausgeprägter Begleitschädigung des Plexus lumbosacralis zuzog. Zur operativen Versorgung der Becken- und Blasenverletzung waren mehrere aufwendige Eingriffe nötig. Auf Grundlage eines Infektes kam es schließlich zur Wundheilungsstörung mit der Notwendigkeit einer Lappenplastik. Der Fall verdeutlicht die Komplexität dieser Verletzung und belegt die Notwendigkeit der interdisziplinären individualisierten Behandlung.
Keywords: Bladder injury; Genitourinary system; Nerve injury; Pelvic ring fracture; Pelvic trauma.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Similar articles
-
[Associated injuries in severe pelvic trauma].Unfallchirurg. 2000 Jul;103(7):572-81. doi: 10.1007/s001130050585. Unfallchirurg. 2000. PMID: 10969545 German.
-
[Urogenital trauma associated with pelvic ring fractures].Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2010 Feb;77(1):18-23. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2010. PMID: 20214856 Czech.
-
Proposed mechanisms of lower urinary tract injury in fractures of the pelvic ring.BJU Int. 2007 Sep;100(3):567-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2007.07020.x. Epub 2007 Jul 3. BJU Int. 2007. PMID: 17608826
-
[Radiological diagnosis of pelvic ring fractures].Radiologe. 2020 Mar;60(3):226-246. doi: 10.1007/s00117-020-00656-8. Radiologe. 2020. PMID: 32108247 Review. German.
-
Pelvic and bladder trauma: a case report and subject review.J Orthop Trauma. 1996;10(5):351-4. doi: 10.1097/00005131-199607000-00011. J Orthop Trauma. 1996. PMID: 8814578 Review.
References
-
- Bosch U, Pohlemann T, Haas N, Tscherne H. Klassifikation und Management des komplexes Beckentraumas. Unfallchirurg. 1992;95:189. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous