Electroactive biofilms: how microbial electron transfer enables bioelectrochemical applications
- PMID: 35381088
- PMCID: PMC9338886
- DOI: 10.1093/jimb/kuac012
Electroactive biofilms: how microbial electron transfer enables bioelectrochemical applications
Abstract
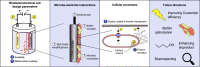
Microbial biofilms are ubiquitous. In marine and freshwater ecosystems, microbe-mineral interactions sustain biogeochemical cycles, while biofilms found on plants and animals can range from pathogens to commensals. Moreover, biofouling and biocorrosion represent significant challenges to industry. Bioprocessing is an opportunity to take advantage of biofilms and harness their utility as a chassis for biocommodity production. Electrochemical bioreactors have numerous potential applications, including wastewater treatment and commodity production. The literature examining these applications has demonstrated that the cell-surface interface is vital to facilitating these processes. Therefore, it is necessary to understand the state of knowledge regarding biofilms' role in bioprocessing. This mini-review discusses bacterial biofilm formation, cell-surface redox interactions, and the role of microbial electron transfer in bioprocesses. It also highlights some current goals and challenges with respect to microbe-mediated bioprocessing and future perspectives.
Keywords: Bioelectrochemical systems; Biofilms; Extracellular electron transfer; Extracellular electron uptake; Microbial electrosynthesis.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Society of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology.
Figures
References
-
- Al Rowaihi I. S., Paillier A., Rasul S., Karan R., Grötzinger S. W., Takanabe K., Eppinger J. (2018). Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) production in an integrated electromicrobial setup: Investigation under stress-inducing conditions. Plos One, 13 (4), e0196079. %10.1371/journal.pone.0196079 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anwer A. H., Khan N., Khan M. D., Shakeel S., Khan M. Z. (2021). Redox mediators as cathode catalyst to boost the microbial electro-synthesis of biofuel product from carbon dioxide. Fuel, 302, 121124. %10.1016/j.fuel.2021.121124 - DOI
-
- Aryal N., Wan L., Overgaard M. H., Stoot A. C., Chen Y., Tremblay P.-L., Zhang T. (2019). Increased carbon dioxide reduction to acetate in a microbial electrosynthesis reactor with a reduced graphene oxide-coated copper foam composite cathode. Bioelectrochemistry, 128, 83–93. %10.1016/j.bioelechem.2019.03.011 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

