Motion corrected silent ZTE neuroimaging
- PMID: 35381110
- PMCID: PMC9321117
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.29201
Motion corrected silent ZTE neuroimaging
Abstract
Purpose: To develop self-navigated motion correction for 3D silent zero echo time (ZTE) based neuroimaging and characterize its performance for different types of head motion.
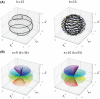
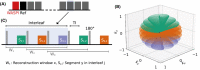
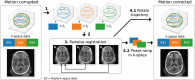
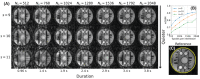
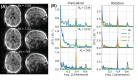
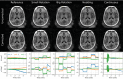
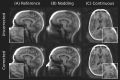
Methods: The proposed method termed MERLIN (Motion Estimation & Retrospective correction Leveraging Interleaved Navigators) achieves self-navigation by using interleaved 3D phyllotaxis k-space sampling. Low resolution navigator images are reconstructed continuously throughout the ZTE acquisition using a sliding window and co-registered in image space relative to a fixed reference position. Rigid body motion corrections are then applied retrospectively to the k-space trajectory and raw data and reconstructed into a final, high-resolution ZTE image.
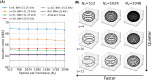
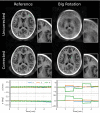
Results: MERLIN demonstrated successful and consistent motion correction for magnetization prepared ZTE images for a range of different instructed motion paradigms. The acoustic noise response of the self-navigated phyllotaxis trajectory was found to be only slightly above ambient noise levels (<4 dBA).
Conclusion: Silent ZTE imaging combined with MERLIN addresses two major challenges intrinsic to MRI (i.e., subject motion and acoustic noise) in a synergistic and integrated manner without increase in scan time and thereby forms a versatile and powerful framework for clinical and research MR neuroimaging applications.
Keywords: RUFIS; ZTE; motion correction; neuroimaging; silent MRI.
© 2022 The Authors. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures

References
-
- Nguyen XV, Tahir S, Bresnahan BW, et al. Prevalence and financial impact of claustrophobia, anxiety, patient motion, and other patient events in magnetic resonance imaging. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2020;29:125‐130. - PubMed
-
- Foster JR, Hall DA, Summerfield AQ, Palmer AR, Bowtell RW. Sound‐level measurements and calculations of safe noise dosage during EPI at 3 T. J of Magn Reson Imaging. 2000;12:157‐163. - PubMed
-
- Sartoretti E, Sartoretti T, Wyss M, van Smoorenburg L, van der Duim S, Cereghetti D, Binkert CA, Sartoretti‐Schefer S, Najafi A, et al. Impact of acoustic noise reduction on patient experience in routine clinical magnetic resonance imaging. Acad Radiol. 2022;29:269‐276. - PubMed
-
- Andre JB, Bresnahan BW, Mossa‐Basha M, et al. Toward quantifying the prevalence, severity, and cost associated with patient motion during clinical MR examinations. J Am Coll Radiol. 2015;12:689‐695. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

