"Selective" serotonin 5-HT2A receptor antagonists
- PMID: 35381208
- PMCID: PMC9252399
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115028
"Selective" serotonin 5-HT2A receptor antagonists
Abstract
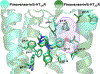
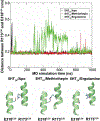
Blockade of the serotonin 5-HT2A G protein-coupled receptor (5-HT2AR) is a fundamental pharmacological characteristic of numerous antipsychotic medications, which are FDA-approved to treat schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and as adjunctive therapies in major depressive disorder. Meanwhile, activation of the 5-HT2AR by serotonergic psychedelics may be useful in treating neuropsychiatric indications, including major depressive and substance use disorders. Serotonergic psychedelics and other 5-HT2AR agonists, however, often bind other receptors, and standard 5-HT2AR antagonists lack sufficient selectivity to make well-founded mechanistic conclusions about the 5-HT2AR-dependent effects of these compounds and the general neurobiological function of 5-HT2ARs. This review discusses the limitations and strengths of currently available "selective" 5-HT2AR antagonists, the molecular determinants of antagonist selectivity at 5-HT2ARs, and the utility of molecular pharmacology and computational methods in guiding the discovery of novel unambiguously selective 5-HT2AR antagonists.
Keywords: 5-HT(2A); Antagonist; Antipsychotic; GPCR; Selectivity.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
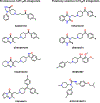

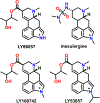
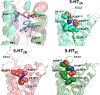
References
-
- Burns CM, Chu H, Rueter SM, Hutchinson LK, Canton H, Sanders-Bush E, et al. Regulation of serotonin-2C receptor G-protein coupling by RNA editing. Nature. 1997; 387(6630): 303–8. - PubMed
-
- Isles AR. Htr2c Splice Variants and 5HT2CR-Mediated Appetite. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2017; 28(8): 542–4. - PubMed
-
- Leysen JE, Niemegeers CJ, Tollenaere JP, Laduron PM. Serotonergic component of neuroleptic receptors. Nature. 1978; 272(5649): 168–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

