RADx Tech Viability and Steering Panels: A Model for MedTech Translational Grant Review
- PMID: 35382011
- PMCID: PMC8901017
- DOI: 10.1109/ojemb.2021.3070821
RADx Tech Viability and Steering Panels: A Model for MedTech Translational Grant Review
Abstract
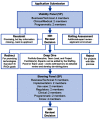
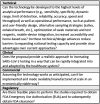
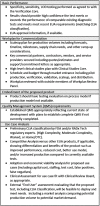
RADxSM Tech's mission is to rapidly accelerate deployment of SARS-CoV-2 tests and could not utilize typical grant application and review processes that can run 4 to 6 months. Instead, RADx Tech leveraged methodologies developed by CIMIT and utilized by POCTRN as described further in this special issue. RADx Tech uses a multi-stage review with two review panels, a Viability Panel and a Steering Panel, that are supported by subject matter experts and a Deep Dive team. Members of the panels have extensive commercialization and business experience in addition to scientific and technical knowledge. The Viability Panel is responsible for assessing whether the proposal is a good fit with the RADx Tech Program and whether it should be recommended to move into a Deep Dive. Less detailed information is requested in the application than a typical SBIR application since the application is refined and details added during the Deep Dive. The Steering Panel reviews the results from the Deep Dive and decides whether to recommend further funding. Everyone on the Viability Panel and Steering Panel reviews every application, thereby providing consistency and context for the reviewers. Utilization of an "assess, improve, and then select" process with review panels comprised of highly experienced review panel members has resulted in improved timing, efficiency, and effectiveness of reviews and has the potential to be extensible beyond RADx Tech.
Keywords: Commercialization; RADx; funding; translational research.
Figures
References
-
- Collins J. M. and Dempsey M. K., “Healthcare innovation methodology: Codifying the process of translating knowledge into better healthcare products, services, and procedures,” Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng., vol. 11, pp. 16–21, Sep. 2019.
-
- Translational Research Institute, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, [Online]. Available: https://tri.uams.edu/about-tri/what-is-translational-research/
-
- Stein E., Lee D., and Gooneratne N., “SBIR/STTR grants: Application guidance,” Academic Entrepreneurship for Med. Health Scientists, vol. 1, no. 2, 2019, Art. no. 9. [Online]. Available: https://repository.upenn.edu/ace/vol1/iss2/9
-
- NIH SBIR/STTR Receipt Dates and Review Schedule, [Online]. Available: https://sbir.nih.gov/apply/submission-dates
-
- National Science Foundation, NSF 17-029, Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for SBIR-STTR, [Online]. Available: https://www.nsf.gov/pubs/2017/nsf17029/nsf17029.jsp
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous