Anti-RNA polymerase III antibodies in patients with suspected and definite systemic sclerosis: Why and how to screen
- PMID: 35382018
- PMCID: PMC8922599
- DOI: 10.1177/2397198318786158
Anti-RNA polymerase III antibodies in patients with suspected and definite systemic sclerosis: Why and how to screen
Abstract
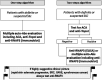
Anti-RNA Polymerase III antibodies are the most frequent anti-nuclear antibodies in systemic sclerosis, after anti-centromere and anti-Topoisomerase I. Considering their specificity for systemic sclerosis, they have been included in 2013 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for systemic sclerosis. They were first identified in 1993 using an immunoprecipitation method; the subsequent diffusion of commercial assays, based on the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay or multiplex line immunoblot techniques, has allowed an increasing number of systemic sclerosis patients to be tested for this autoantibody; nevertheless, the diffusion of this test in systemic sclerosis patients is probably still sub-optimal. Anti-RNA Polymerase III antibodies have been associated with important clinical manifestations: rapid and diffuse cutaneous involvement, joint contractures, scleroderma renal crisis, gastric antral vascular ectasia and malignancies synchronous to systemic sclerosis onset. Moreover, other possible clinical associations, including pulmonary hypertension, still need confirmation. Since the correct approach for screening for anti- RNA Polymerase III antibodies in patients with suspected or definite systemic sclerosis is still debated, possible strategies are proposed here. Moreover, issues that are still controversial are discussed, including the interpretation of multiple simultaneous positivity for anti-RNA Polymerase III antibodies and other autoantibodies in line immunoassay, and the possible relevance of anti-RNA Polymerase III antibodies titre.
Keywords: Autoantibodies; RNA polymerase III; enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; immunoblotting; immunoprecipitation; scleroderma; systemic.
© The Author(s) 2018.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Okano Y, Steen VD, Medsger TA. Autoantibody reactive with RNA polymerase III in systemic sclerosis. Ann Intern Med 1993; 119: 1005–1013. - PubMed
-
- Bunn CC, Denton CP, Shi-Wen X, et al. . Anti-RNA polymerases and other autoantibody specificities in systemic sclerosis. Br J Rheumatol 1998; 37: 15–20. - PubMed
-
- Kuwana M, Okano Y, Pandey JP, et al. . Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of anti-RNA polymerase III antibody: analytical accuracy and clinical associations in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 2005; 52: 2425–2432. - PubMed
-
- Kuwana M. A to-do list at diagnosis of systemic sclerosis with positive anti-RNA polymerase III antibodies. J Rheumatol 2017; 44: 550–552. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources