Combination therapy with bosentan and sildenafil for refractory digital ulcers and Raynaud's phenomenon in a 30-year-old woman with systemic sclerosis: Case report and literature review
- PMID: 35382024
- PMCID: PMC8922606
- DOI: 10.1177/2397198319876738
Combination therapy with bosentan and sildenafil for refractory digital ulcers and Raynaud's phenomenon in a 30-year-old woman with systemic sclerosis: Case report and literature review
Abstract
Background: Systemic sclerosis is a rare autoimmune disease characterized by skin and organ fibrosis, and vasculopathy. Raynaud's phenomenon is almost universally present in systemic sclerosis and can be the most debilitating symptom. Raynaud's phenomenon may lead to the development of digital ulcers, potentially complicated by infection, tissue necrosis, and auto-amputation. Recommended treatments have variable efficacy.
Methods: We report the case of a 30-year-old woman with diffuse systemic sclerosis suffering from severe Raynaud's phenomenon and digital ulcers with digital tissue necrosis who was treated with combination therapy of an endothelin receptor antagonist and phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor. In addition, we reviewed the literature on the topic.
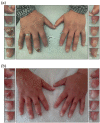
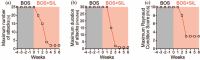
Results: Previous therapy with calcium-channel blockers, intravenous iloprost, and bosentan had all failed to control symptoms. We added sildenafil in combination with bosentan and observed a rapid and sustained treatment effect. Raynaud's phenomenon severity, number of attacks, and attack duration decreased within 2 weeks of initiating treatment. Furthermore, this resulted in the healing of established digital ulcers.
Conclusion: Our case report suggests that combination therapy may be a feasible treatment for the most severely affected and refractory patients. In our literature review, we found one retrospective study and three additional cases with similarly encouraging results.
Keywords: Raynaud’s phenomenon; digital ulcers; endothelin receptor antagonists; phosphodiesterase inhibitors; systemic sclerosis.
© The Author(s) 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Management of Raynaud's phenomenon in systemic sclerosis-a practical approach.J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2019 Jun;4(2):102-110. doi: 10.1177/2397198318823951. Epub 2019 Jan 28. J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2019. PMID: 35382396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Raynaud's phenomenon and digital ischaemia--pharmacologic approach and alternative treatment options.Vasa. 2016;45(3):201-12. doi: 10.1024/0301-1526/a000526. Vasa. 2016. PMID: 27129065 Review.
-
The Relationship between Smoking, Raynaud's Phenomenon, Digital Ulcers, and Skin Thickness in the Waikato Systemic Sclerosis Cohort.Rheumatol Immunol Res. 2022 Jul 6;3(2):84-89. doi: 10.2478/rir-2022-0014. eCollection 2022 Jun. Rheumatol Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 36465326 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelin Receptor Antagonists for the Treatment of Raynaud's Phenomenon and Digital Ulcers in Systemic Sclerosis.Int J Rheumatol. 2011;2011:201787. doi: 10.1155/2011/201787. Epub 2011 Oct 27. Int J Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 22121371 Free PMC article.
-
Rheopheresis for Digital Ulcers and Raynaud's Phenomenon in Systemic Sclerosis Refractory to Conventional Treatments.Front Med (Lausanne). 2019 Sep 18;6:208. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2019.00208. eCollection 2019. Front Med (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 31620442 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Multifaceted Potential of Sildenafil in Medicine.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Dec 17;59(12):2190. doi: 10.3390/medicina59122190. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 38138293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Raynaud's Phenomenon: A Current Update on Pathogenesis, Diagnostic Workup, and Treatment.Vasc Specialist Int. 2024 Jul 23;40:26. doi: 10.5758/vsi.240047. Vasc Specialist Int. 2024. PMID: 39040029 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allanore Y, Simms R, Distler O, et al. Systemic sclerosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2015; 23(1): 15002. - PubMed
-
- Meier FMP, Frommer KW, Dinser R, et al. Update on the profile of the EUSTAR cohort: an analysis of the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research group database. Ann Rheum Dis 2012; 71(8): 1355–1360. - PubMed
-
- Brand M, Hollaender R, Rosenberg D, et al. An observational cohort study of patients with newly diagnosed digital ulcer disease secondary to systemic sclerosis registered in the EUSTAR database. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2015; 33(4 Suppl. 91): S47–S54. - PubMed
-
- Tyndall AJ, Bannert B, Vonk M, et al. Causes and risk factors for death in systemic sclerosis: a study from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) database. Ann Rheum Dis 2010; 69(10): 1809–1815. - PubMed
-
- Hughes M, Herrick AL. Digital ulcers in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2017; 56(1): 14–25. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
