Intrinsic neural activity predisposes susceptibility to a body illusion
- PMID: 35382092
- PMCID: PMC8976633
- DOI: 10.1093/texcom/tgac012
Intrinsic neural activity predisposes susceptibility to a body illusion
Abstract
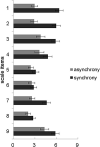
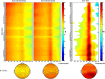
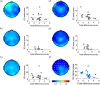
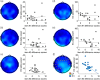
Susceptibility to the rubber hand illusion (RHI) varies. To date, however, there is no consensus explanation of this variability. Previous studies, focused on the role of multisensory integration, have searched for neural correlates of the illusion. But those studies have failed to identify a sufficient set of functionally specific neural correlates. Because some evidence suggests that frontal α power is one means of tracking neural instantiations of self, we hypothesized that the higher the frontal α power during the eyes-closed resting state, the more stable the self. As a corollary, we infer that the more stable the self, the less susceptible are participants to a blurring of boundaries-to feeling that the rubber hand belongs to them. Indeed, we found that frontal α amplitude oscillations negatively correlate with susceptibility. Moreover, since lower frequencies often modulate higher frequencies, we explored the possibility that this might be the case for the RHI. Indeed, some evidence suggests that high frontal α power observed in low-RHI participants is modulated by δ frequency oscillations. We conclude that while neural correlates of multisensory integration might be necessary for the RHI, sufficient explanation involves variable intrinsic neural activity that modulates how the brain responds to incompatible sensory stimuli.
Keywords: EEG; intrinsic neural activity; rubber hand illusion; self-relatedness; α band power.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neurophysiological Correlates of the Rubber Hand Illusion in Late Evoked and Alpha/Beta Band Activity.Front Hum Neurosci. 2017 Jul 25;11:377. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2017.00377. eCollection 2017. Front Hum Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28790906 Free PMC article.
-
Anodal transcranial direct current stimulation over the posterior parietal cortex reduces the onset time to the rubber hand illusion and increases the body ownership.Exp Brain Res. 2018 Nov;236(11):2935-2943. doi: 10.1007/s00221-018-5353-9. Epub 2018 Aug 6. Exp Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 30084055
-
Rubber hand illusion modulates the influences of somatosensory and parietal inputs to the motor cortex.J Neurophysiol. 2019 Feb 1;121(2):563-573. doi: 10.1152/jn.00345.2018. Epub 2019 Jan 9. J Neurophysiol. 2019. PMID: 30625001
-
The rubber hand universe: On the impact of methodological differences in the rubber hand illusion.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2019 Sep;104:268-280. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2019.07.008. Epub 2019 Jul 20. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2019. PMID: 31336114 Review.
-
Perspectives and possible applications of the rubber hand and virtual hand illusion in non-invasive rehabilitation: technological improvements and their consequences.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2014 Jul;44:33-44. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.02.013. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2014. PMID: 24661983 Review.
Cited by
-
Revisiting the relationship between illusory hand ownership induced by visuotactile synchrony and cardiac interoceptive accuracy.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 10;13(1):17132. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-43990-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37816882 Free PMC article.
-
Neural bases of the bodily self as revealed by electrical brain stimulation: A systematic review.Hum Brain Mapp. 2023 May;44(7):2936-2959. doi: 10.1002/hbm.26253. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Hum Brain Mapp. 2023. PMID: 36852645 Free PMC article.
-
Eyes-Open and Eyes-Closed Resting State Network Connectivity Differences.Brain Sci. 2023 Jan 10;13(1):122. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13010122. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 36672103 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying EEG biomarkers of sense of embodiment in virtual reality: insights from spatio-spectral features.Front Neuroergon. 2025 May 12;6:1572851. doi: 10.3389/fnrgo.2025.1572851. eCollection 2025. Front Neuroergon. 2025. PMID: 40420994 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bai Y, Nakao T, Xu J, Qin P, Chaves P, Heinzel A, Duncan N, Lane TJ, Yen NS, Tsai SY, et al. Resting state glutamate predicts elevated pre-stimulus alpha during self-relatedness: a combined EEG-MRS study on “rest-self overlap”. Soc Neurosci. 2016:11(3):249–263. 10.1080/17470919.2015.1072582. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bekrater-Bodmann R, Foell J, Diers M, Kamping S, Rance M, Kirsch P, Trojan J, Fuchs X, Bach F, Çakmak HK, et al. The importance of synchrony and temporal order of visual and tactile input for illusory limb ownership experiences? An fMRI study applying virtual reality. PLoS One. 2014:9(1):e87013. 10.1371/journal.pone.0087013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B Methodol. 1995:57(1):289–300. 10.1111/J.2517-6161.1995.TB02031.X. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
