Piezo1 Is a Mechanosensor Channel in Central Nervous System Capillaries
- PMID: 35382561
- PMCID: PMC9106929
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.320827
Piezo1 Is a Mechanosensor Channel in Central Nervous System Capillaries
Abstract
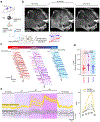
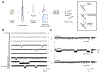
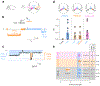
Capillaries are equipped to sense neurovascular coupling agents released onto the outer wall of a capillary, translating these external signals into electrical/Ca2+ changes that play a crucial role in blood flow regulation and ensuring that neuronal demands are met. However, control mechanisms attributable to forces imposed onto the lumen are less clear. Here, we show that Piezo1 channels act as mechanosensors in central nervous system capillaries. Electrophysiological analyses confirmed expression and function of Piezo1 channels in brain cortical and retinal capillaries. Activation of Piezo1 channels evoked currents that were sensitive to endothelial cell-specific Piezo1 deletion. Using genetically encoded Ca2+ indicator mice and an ex vivo pressurized retina preparation, we found that activation of Piezo1 channels by mechanical forces triggered Ca2+ signals in capillary endothelial cells. Collectively, these findings indicate that Piezo1 channels are capillary mechanosensors that initiate crucial Ca2+ signals and could, therefore, have a profound impact on central nervous system blood flow control.
Keywords: Piezo1; calcium signaling; capillaries; central nervous system; endothelial cells; neurovascular coupling.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
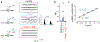


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F32 HL152576/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL121706/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM135007/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL095488/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL140027/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 17POST33650030/AHA/American Heart Association-American Stroke Association/United States
- 20CDA35310097 - OSAMA HARRAZ/AHA/American Heart Association-American Stroke Association/United States
- R37 DK053832/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL131181/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS110656/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

