Identification of host-pathogen-disease relationships using a scalable multiplex serology platform in UK Biobank
- PMID: 35383168
- PMCID: PMC8983701
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-29307-3
Identification of host-pathogen-disease relationships using a scalable multiplex serology platform in UK Biobank
Abstract
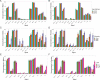
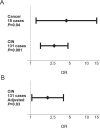
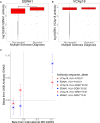
Certain infectious agents are recognised causes of cancer and other chronic diseases. To understand the pathological mechanisms underlying such relationships, here we design a Multiplex Serology platform to measure quantitative antibody responses against 45 antigens from 20 infectious agents including human herpes, hepatitis, polyoma, papilloma, and retroviruses, as well as Chlamydia trachomatis, Helicobacter pylori and Toxoplasma gondii, then assayed a random subset of 9695 UK Biobank participants. We find seroprevalence estimates consistent with those expected from prior literature and confirm multiple associations of antibody responses with sociodemographic characteristics (e.g., lifetime sexual partners with C. trachomatis), HLA genetic variants (rs6927022 with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) EBNA1 antibodies) and disease outcomes (human papillomavirus-16 seropositivity with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, and EBV responses with multiple sclerosis). Our accessible dataset is one of the largest incorporating diverse infectious agents in a prospective UK cohort offering opportunities to improve our understanding of host-pathogen-disease relationships with significant clinical and public health implications.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Meeting IWGotEoCRtH. A review of human carcinogens. International Agency for Research on Cancer (2012).
-
- Young LS, Yap LF, Murray PG. Epstein-Barr virus: more than 50 years old and still providing surprises. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2016;16:789–802. - PubMed
-
- Gkrania-Klotsas E, et al. Higher immunoglobulin G antibody levels against cytomegalovirus are associated with incident ischemic heart disease in the population-based EPIC-Norfolk cohort. J. Infect. Dis. 2012;206:1897–1903. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- MR/S023380/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_QA137853/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 106289/Z/14/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_17228/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_15067/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_17223/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CH/1996001/9454/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_12027/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 203141/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- MC_EX_G0801669/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_21051/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U137686854/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_12029/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0300622/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_12028/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_18026/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

