An MMP-degraded and cross-linked fragment of type III collagen as a non-invasive biomarker of hepatic fibrosis resolution
- PMID: 35384259
- PMCID: PMC9324161
- DOI: 10.1111/liv.15270
An MMP-degraded and cross-linked fragment of type III collagen as a non-invasive biomarker of hepatic fibrosis resolution
Abstract
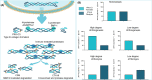
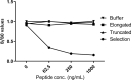
Background and aims: Liver fibrosis results from a prolonged wound healing response to continued injury with excessive production of extracellular proteins. In patients with chronic liver disease, the monitoring of liver fibrosis dynamics is of high interest. Whilst markers of fibrogenesis exist, markers of hepatic fibrosis resolution remain an unmet clinical need. Thus, we sought to develop an assay quantifying a circulating proteolytic fragment of cross-linked type III collagen as a biomarker of fibrolysis, testing its utility in two clinical cohorts of liver fibrosis of distinct aetiology and regressing endotype METHODS: We used a monoclonal antibody targeting the C-telopeptide of type III collagen following C-proteinase cleavage to develop and validate a neo-epitope-specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (CTX-III). A potential fibrosis resolution marker, CTX-III, was measured in two clinical cohorts of patients with obesity-associated non-alcoholic fatty liver disease undergoing bariatric surgery or hepatitis C virus infection from a clinical trial study evaluating the anti-fibrotic effect of farglitazar.
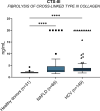
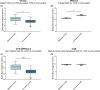
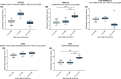
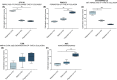
Results: CTX-III was robust and specific for the targeted neo-epitope with good reproducibility in EDTA plasma. We assessed type III collagen remodelling using a panel of biomarkers, including a type III collagen formation marker (PRO-C3), degradation (C3M), and CTX-III (fibrolysis). Net fibrolysis was increased in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease following bariatric surgery (p < .001). Moreover, net fibrolysis identified spontaneous fibrotic regressors from stable and progressors (p < .05 and p < .001) among hepatitis C virus infection patients.
Conclusion: Circulating CTX-III as a marker of fibrolysis indicates the biomarker's beneficial use in assessing hepatic fibrosis resolution.
Keywords: collagen cross-linking; fibrosis resolution; hepatic fibrosis; non-invasive biomarkers.
© 2022 Nordic Bioscience. Liver International published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Martin Pehrsson, Shu Sun, Ida Falk Villesen, Mette Juul Nielsen and Joachim Høg Mortensen are employed at Nordic Bioscience A/S, a company involved in the discovery and development of biochemical biomarkers. Tina Manon‐Jensen, Anne‐Christine Bay‐Jensen, Diana Julie Leeming and Morten Asser Karsdal are employed at and own stocks in Nordic Bioscience A/S. Helena Castañé, Jorge Joven, Keyur Patel and Zachary Goodman have no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

