Genome-wide DNA methylation profiling confirms a case of low-level mosaic Kabuki syndrome 1
- PMID: 35384273
- PMCID: PMC9321966
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.a.62754
Genome-wide DNA methylation profiling confirms a case of low-level mosaic Kabuki syndrome 1
Abstract
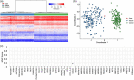
Kabuki syndrome is a Mendelian disorder of the epigenetic machinery characterized by typical dysmorphic features, intellectual disability, and postnatal growth deficiency. Pathogenic variants in the genes encoding the chromatin modifiers KMT2D and KDM6A are responsible for Kabuki syndrome 1 (KS1) and Kabuki syndrome 2 (KS2), respectively. In addition, 11 cases of KS1 caused by mosaic variants in KMT2D have been reported in the literature. Some of these individuals display milder craniofacial and growth phenotypes, and most do not have congenital heart defects. We report the case of an infant with severe hypoplastic left heart syndrome with mitral atresia and aortic atresia (HLHS MA-AA), pulmonary vein stenosis, and atypical facies with a somatic mosaic de novo nonsense variant in KMT2D (c.8200C>T, p.R2734*) identified on trio exome sequencing of peripheral blood and present in 11.2% of sequencing reads. KS was confirmed with EpiSign, a diagnostic genome-wide DNA methylation platform used to identify epigenetic signatures. This case suggests that use of this newly available clinical test can guide the interpretation of low-level mosaic variants identified through sequencing and suggests a new lower limit of mosaicism in whole blood required for a diagnosis of KS.
Keywords: DNA methylation; HLHS (hypoplastic left heart syndrome); KMT2D; Kabuki syndrome; episignature; mosaicism.
© 2022 The Authors. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures

References
-
- Adam, M. P. , Banka, S. , Bjornsson, H. T. , Bodamer, O. , Chudley, A. E. , Harris, J. , Kawame, H. , Lanpher, B. C. , Lindsley, A. W. , Merla, G. , Miyake, N. , Okamoto, N. , Stumpel, C. T. , Niikawa, N. , & Board, K. S. M. A. (2019). Kabuki syndrome: International consensus diagnostic criteria. Journal of Medical Genetics, 56(2), 89–95. - PubMed
-
- Aref‐Eshghi, E. , Bend, E. G. , Colaiacovo, S. , Caudle, M. , Chakrabarti, R. , Napier, M. , Brick, L. , Brady, L. , Carere, D. A. , Levy, M. A. , Kerkhof, J. , Stuart, A. , Saleh, M. , Beaudet, A. L. , Li, C. , Kozenko, M. , Karp, N. , Prasad, C. , Siu, V. M. , … Sadikovic, B. (2019). Diagnostic utility of genome‐wide DNA methylation testing in genetically unsolved individuals with suspected hereditary conditions. American Journal of Human Genetics, 104(4), 685–700. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aref‐Eshghi, E. , Bourque, D. K. , Kerkhof, J. , Carere, D. A. , Ainsworth, P. , Sadikovic, B. , Armour, C. M. , & Lin, H. (2019). Genome‐wide DNA methylation and RNA analyses enable reclassification of two variants of uncertain significance in a patient with clinical Kabuki syndrome. Human Mutation, 40(10), 1684–1689. - PubMed
-
- Aref‐Eshghi, E. , Kerkhof, J. , Pedro, V. P. , Groupe, D. I. F. , Barat‐Houari, M. , Ruiz‐Pallares, N. , Andrau, J. C. , Lacombe, D. , Van‐Gils, J. , Fergelot, P. , Dubourg, C. , Cormier‐Daire, V. , Rondeau, S. , Lecoquierre, F. , Saugier‐Veber, P. , Nicolas, G. , Lesca, G. , Chatron, N. , Sanlaville, D. , … Sadikovic, B. (2020). Evaluation of DNA methylation episignatures for diagnosis and phenotype correlations in 42 Mendelian neurodevelopmental disorders. American Journal of Human Genetics, 106(3), 356–370. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aref‐Eshghi, E. , Rodenhiser, D. I. , Schenkel, L. C. , Lin, H. , Skinner, C. , Ainsworth, P. , Pare, G. , Hood, R. L. , Bulman, D. E. , Kernohan, K. D. , Care4Rare Canada Consortium , Boycott, K. M. , Campeau, P. M. , Schwartz, C. , & Sadikovic, B. (2018). Genomic DNA methylation signatures enable concurrent diagnosis and clinical genetic variant classification in neurodevelopmental syndromes. American Journal of Human Genetics, 102(1), 156–174. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

