BSCL2/Seipin deficiency in hearts causes cardiac energy deficit and dysfunction via inducing excessive lipid catabolism
- PMID: 35384404
- PMCID: PMC8982503
- DOI: 10.1002/ctm2.736
BSCL2/Seipin deficiency in hearts causes cardiac energy deficit and dysfunction via inducing excessive lipid catabolism
Abstract
Background: Heart failure (HF) is one of the leading causes of death worldwide and is associated with cardiac metabolic perturbations. Human Type 2 Berardinelli-Seip Congenital Lipodystrophy (BSCL2) disease is caused by mutations in the BSCL2 gene. Global lipodystrophic Bscl2-/- mice exhibit hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with reduced cardiac steatosis. Whether BSCL2 plays a direct role in regulating cardiac substrate metabolism and/or contractile function remains unknown.
Methods: We generated mice with cardiomyocyte-specific deletion of Bscl2 (Bscl2cKO ) and studied their cardiac substrate utilisation, bioenergetics, lipidomics and contractile function under baseline or after either a treatment regimen using fatty acid oxidation (FAO) inhibitor trimetazidine (TMZ) or a prevention regimen with high-fat diet (HFD) feeding. Mice with partial ATGL deletion and cardiac-specific deletion of Bscl2 were also generated followed by cardiac phenotyping.
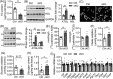
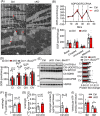
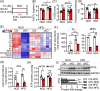
Results: Different from hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in Bscl2-/- mice, mice with cardiac-specific deletion of Bscl2 developed systolic dysfunction with dilation. Myocardial BSCL2 deletion led to elevated ATGL expression and FAO along with reduced cardiac lipid contents. Cardiac dysfunction in Bscl2cKO mice was independent of mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress, but associated with decreased metabolic reserve and ATP levels. Importantly, cardiac dysfunction in Bscl2cKO mice could be partially reversed by FAO inhibitor TMZ, or prevented by genetic abolishment of one ATGL allele or HFD feeding. Lipidomic analysis further identified markedly reduced glycerolipids, glycerophospholipids, NEFA and acylcarnitines in Bscl2cKO hearts, which were partially normalised by TMZ or HFD.
Conclusions: We identified a new form of cardiac dysfunction with excessive lipid utilisation which ultimately causes cardiac substrate depletion and bioenergetics failure. Our findings also uncover a crucial role of BSCL2 in controlling cardiac lipid catabolism and contractile function and provide novel insights into metabolically treating energy-starved HF using FAO inhibitor or HFD.
Keywords: BSCL2/Seipin; heart failure; lipid metabolism; lipidomics.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Shanghai Institute of Clinical Bioinformatics.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures




References
-
- van der Vusse GJ, Glatz JF, Stam HC, Reneman RS. Fatty acid homeostasis in the normoxic and ischemic heart. Physiol Rev. 1992;72:881–940. - PubMed
-
- Ingwall JS, Weiss RG. Is the failing heart energy starved? On using chemical energy to support cardiac function. Circ Res. 2004;95:135–145. - PubMed
-
- Neubauer S, Horn M, Cramer M, et al. Myocardial phosphocreatine‐to‐ATP ratio is a predictor of mortality in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 1997;96:2190–2196. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
