Interleukin-1 Mediates Ischemic Brain Injury via Induction of IL-17A in γδ T Cells and CXCL1 in Astrocytes
- PMID: 35384588
- PMCID: PMC9684245
- DOI: 10.1007/s12017-022-08709-y
Interleukin-1 Mediates Ischemic Brain Injury via Induction of IL-17A in γδ T Cells and CXCL1 in Astrocytes
Abstract
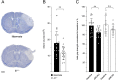
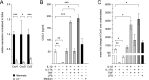
As a prototypical proinflammatory cytokine, interleukin-1 (IL-1) exacerbates the early post-stroke inflammation, whereas its neutralization is protective. To further investigate the underlying cell-type-specific IL-1 effects, we subjected IL-1 (α/β) knockout (Il1-/-) and wildtype (WT) littermate mice to permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion (pMCAO) and assessed immune cell infiltration and cytokine production in the ischemic hemisphere by flow cytometry 24 h and 72 h after stroke. Il1-/- mice showed smaller infarcts and reduced neutrophil infiltration into the ischemic brain. We identified γδ T cells and astrocytes as target cells of IL-1 signaling-mediated neutrophil recruitment. First, IL-1-induced IL-17A production in γδ T cells in vivo, and IL-17A enhanced the expression of the main neutrophil attracting chemokine CXCL1 by astrocytes in the presence of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in vitro. Second, IL-1 itself was a potent activator of astrocytic CXCL1 production in vitro. By employing a novel FACS sorting strategy for the acute isolation of astrocytes from ischemic brains, we confirmed that IL-1 is pivotal for Cxcl1 upregulation in astrocytes in vivo. Our results underscore the pleiotropic effects of IL-1 on immune and non-immune cells within the CNS to mount and amplify the post-stroke inflammatory response.
Keywords: Astrocytes; CXCL1; Inflammation; Interleukin-1; Interleukin-17A; Ischemic stroke; γδ T cells.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Allen C, Thornton P, Denes A, McColl BW, Pierozynski A, Monestier M, Pinteaux E, Rothwell NJ, Allan SM. Neutrophil cerebrovascular transmigration triggers rapid neurotoxicity through release of proteases associated with decondensed DNA. The Journal of Immunology. 2012;189(1):381–392. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200409. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arumugam TV, Chan SL, Jo DG, Yilmaz G, Tang SC, Cheng A, Gleichmann M, Okun E, Dixit VD, Chigurupati S, Mughal MR, Ouyang X, Miele L, Magnus T, Poosala S, Granger DN, Mattson MP. Gamma secretase-mediated Notch signaling worsens brain damage and functional outcome in ischemic stroke. Nature Medicine. 2006;12(6):621–623. doi: 10.1038/nm1403. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bach A, Clausen BH, Møller M, Vestergaard B, Chi CN, Round A, Sørensen PL, Nissen KB, Kastrup JS, Gajhede M, Jemth P, Kristensen AS, Lundström P, Lambertsen KL, Strømgaard K. A high-affinity, dimeric inhibitor of PSD-95 bivalently interacts with PDZ1-2 and protects against ischemic brain damage. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2012;109(9):3317–3322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1113761109. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Batiuk MY, De Vin F, Duqué SI, Li C, Saito T, Saido T, Fiers M, Belgard TG, Holt MG. An immunoaffinity-based method for isolating ultrapure adult astrocytes based on ATP1B2 targeting by the ACSA-2 antibody. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2017;292(21):8874–8891. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.765313. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

