A Standardized Investigational Ki-67 Immunohistochemistry Assay Used to Assess High-Risk Early Breast Cancer Patients in the monarchE Phase 3 Clinical Study Identifies a Population With Greater Risk of Disease Recurrence When Treated With Endocrine Therapy Alone
- PMID: 35384873
- PMCID: PMC8989635
- DOI: 10.1097/PAI.0000000000001009
A Standardized Investigational Ki-67 Immunohistochemistry Assay Used to Assess High-Risk Early Breast Cancer Patients in the monarchE Phase 3 Clinical Study Identifies a Population With Greater Risk of Disease Recurrence When Treated With Endocrine Therapy Alone
Abstract
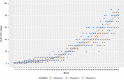
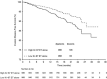
The objectives were to develop a standardized Ki-67 immunohistochemistry (IHC) method for precise, robust, and reproducible assessment of patients with early breast cancer, and utilize this assay to evaluate patients participating in the monarchE study (NCT03155997). The Ki-67 assay was developed and validated for sensitivity, specificity, repeatability, precision, and robustness using a predefined ≥20% cutoff. Reproducibility studies (intersite and intrasite, interobserver and intraobserver) were conducted at 3 external laboratories using detailed scoring instructions designed for monarchE. Using the assay, patient tumors were classified as displaying high (≥20%) or low (<20%) Ki-67 expression; Kaplan-Meier methods evaluated 2-year invasive disease-free survival rates for these 2 groups among patients treated with endocrine therapy (ET) alone. All analytical validation and reproducibility studies achieved point estimates of >90% for negative, positive, and overall percent agreement. Intersite reproducibility produced point estimate values of 94.7%, 100.0%, and 97.3%. External interobserver reproducibility produced point estimate values of 98.9%, 97.8%, and 98.3%. Among 1954 patients receiving ET alone, 986 (50.5%) had high and 968 (49.5%) had low Ki-67 expression. Patients with high Ki-67 had a clinically meaningful increased risk of developing invasive disease within 2 years compared with those with low Ki-67 [2-y invasive disease-free survival rate: 86.1% (95% confidence interval: 83.1%-88.7%) vs. 92.0% (95% confidence interval: 89.7%-93.9%), respectively]. This standardized Ki-67 methodology resulted in high concordance across multiple laboratories, and its use in the monarchE study prospectively demonstrated the prognostic value of Ki-67 IHC in HR+, HER2- early breast cancer with high-risk clinicopathologic features.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
M.D.P. is an employee and company stockholder at Agilent Technologies; she also reports her spouse, Gregory Cherryholmes, is an employee and company stockholder for Agilent Technologies. G.B.N. is an employee and company stockholder at Agilent Technologies; she also reports her spouse, Jon St. Onge, is an employee and company stockholder at Agilent Technologies. Y.G. is former employee of Agilent technologies, and company stockholder. A.T.W. owns stock in Agilent Technologies. G.G. has nothing to disclose. S.T.-F. is an employee and company stockholder at Agilent Technologies. M.C. has nothing to disclose. M.M. is a former employee and minor company stockholder at Eli Lilly and Company, and a current employee at ImmunoGen; all work for this manuscript was completed while he was employed at Eli Lilly and Company. M.F.P. reports receiving honoraria from Science Branding Communications; serving on a Scientific Advisory Board and receiving consulting fees from Biocartis, Eli Lilly and Company, Merck, AstraZeneca, and Novartis; serving as a consultant with consulting fees from Zymeworks Inc; serving as a consultant and having private equity from TORL Biotherapeutics LLC; serving on a Medical Advisory Board and receiving consulting fees from Cepheid; and serving on a Pathology Advisory Board and receiving consulting fees from Eli Lilly and Company, USA. C.G. is an employee and company stockholder at Agilent Technologies. A.M.G. is an employee and company stockholder at Eli Lilly and Company; he also reports his spouse is an employee of Eli Lilly and Company. D.H. declares no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Smith I, Robertson J, Kilburn L, et al. . Long-term outcome and prognostic value of Ki-67 after periopertative endocrine therapy in postmenopausal women with hormone-sensitive early breast cancer (POETIC): an open-label, multicentre, parallel-group, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:1443–1454. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sledge GW, Jr, Toi M, Neven P, et al. . MONARCH 2: abemaciclib in combination with fulvestrant in women with HR+/HER2− advanced breast cancer who had progressed while receiving endocrine therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:2875–2884. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

