Deadenylase-dependent mRNA decay of GDF15 and FGF21 orchestrates food intake and energy expenditure
- PMID: 35385705
- PMCID: PMC9386786
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.03.005
Deadenylase-dependent mRNA decay of GDF15 and FGF21 orchestrates food intake and energy expenditure
Abstract
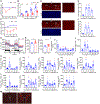
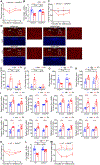
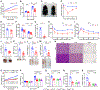
Hepatokines, secretory proteins from the liver, mediate inter-organ communication to maintain a metabolic balance between food intake and energy expenditure. However, molecular mechanisms by which hepatokine levels are rapidly adjusted following stimuli are largely unknown. Here, we unravel how CNOT6L deadenylase switches off hepatokine expression after responding to stimuli (e.g., exercise and food) to orchestrate energy intake and expenditure. Mechanistically, CNOT6L inhibition stabilizes hepatic Gdf15 and Fgf21 mRNAs, increasing corresponding serum protein levels. The resulting upregulation of GDF15 stimulates the hindbrain to suppress appetite, while increased FGF21 affects the liver and adipose tissues to induce energy expenditure and lipid consumption. Despite the potential of hepatokines to treat metabolic disorders, their administration therapies have been challenging. Using small-molecule screening, we identified a CNOT6L inhibitor enhancing GDF15 and FGF21 hepatokine levels, which dramatically improves diet-induced metabolic syndrome. Our discovery, therefore, lays the foundation for an unprecedented strategy to treat metabolic syndrome.
Keywords: CCR4-NOT deadenylase complex; FGF21; GDF15; energy expenditure; food intake; hepatokine; inter-organ communication; mRNA degradation; metabolic syndrome.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Comment in
-
CNOT6L regulates hepatokine expression.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2022 Jul;18(7):392. doi: 10.1038/s41574-022-00684-5. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 35523890 No abstract available.
References
-
- Basquin J, Roudko VV, Rode M, Basquin C, Seraphin B, and Conti E (2012). Architecture of the nuclease module of the yeast Ccr4-not complex: the Not1-Caf1-Ccr4 interaction. Mol Cell 48, 207–218. - PubMed
-
- Bhaskar V, Roudko V, Basquin J, Sharma K, Urlaub H, Seraphin B, and Conti E (2013). Structure and RNA-binding properties of the Not1-Not2-Not5 module of the yeast Ccr4-Not complex. Nat Struct Mol Biol 20, 1281–1288. - PubMed
-
- Boland A, Chen Y, Raisch T, Jonas S, Kuzuoglu-Ozturk D, Wohlbold L, Weichenrieder O, and Izaurralde E (2013). Structure and assembly of the NOT module of the human CCR4-NOT complex. Nat Struct Mol Biol 20, 1289–1297. - PubMed
-
- Chaaban I, Rizk OH, Ibrahim TM, Henen SS, El-Khawass EM, Bayad AE, El-Ashmawy IM, and Nematalla HA (2018). Synthesis, anti-inflammatory screening, molecular docking, and COX-1,2/−5-LOX inhibition profile of some novel quinoline derivatives. Bioorg Chem 78, 220–235. - PubMed
-
- Chang H, Lim J, Ha M, and Kim VN (2014). TAIL-seq: genome-wide determination of poly(A) tail length and 3' end modifications. Mol Cell 53, 1044–1052. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

