Brain-targeting, acid-responsive antioxidant nanoparticles for stroke treatment and drug delivery
- PMID: 35386312
- PMCID: PMC8958421
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.02.033
Brain-targeting, acid-responsive antioxidant nanoparticles for stroke treatment and drug delivery
Abstract
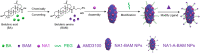
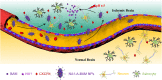
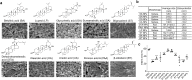
Stroke is the leading cause of death and disability. Currently, there is no effective pharmacological treatment for this disease, which can be partially attributed to the inability to efficiently deliver therapeutics to the brain. Here we report the development of natural compound-derived nanoparticles (NPs), which function both as a potent therapeutic agent for stroke treatment and as an efficient carrier for drug delivery to the ischemic brain. First, we screened a collection of natural nanomaterials and identified betulinic acid (BA) as one of the most potent antioxidants for stroke treatment. Next, we engineered BA NPs for preferential drug release in acidic ischemic tissue through chemically converting BA to betulinic amine (BAM) and for targeted drug delivery through surface conjugation of AMD3100, a CXCR4 antagonist. The resulting AMD3100-conjugated BAM NPs, or A-BAM NPs, were then assessed as a therapeutic agent for stroke treatment and as a carrier for delivery of NA1, a neuroprotective peptide. We show that intravenous administration of A-BAM NPs effectively improved recovery from stroke and its efficacy was further enhanced when NA1 was encapsulated. Due to their multifunctionality and significant efficacy, we anticipate that A-BAM NPs have the potential to be translated both as a therapeutic agent and as a drug carrier to improve the treatment of stroke.
Keywords: A-BAM NPs, A-BAM NPs; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; Acid-triggered release; Antioxidant nanoparticles; BA, betulinic acid; BAM, betulinic amine; BBB, blood brain barrier; BIRDS, biosensor imaging of redundant deviation in shifts; BT, ß-sitosterol; DLS, dynamic light scattering; DTA, dehydrotrametenolic acid; DYDA, diketohydrindylidene diketohydrindamine; Drug delivery; GA, glycyrrhetic acid; Ischemic stroke; LCMS, liquid chromatography mass spectrometry; LP, lupeol; MCAO, middle cerebral artery occlusion; NA1; NMR, nuclear magnetic resonance; NP, nanoparticle; OA, oleanolic acid; PAA, poricoic acid; PEG, polyethylene glycol; SA, sumaresinolic acid; SEM, scanning electron microscopy; ST, stigmasterol; TEM, transmission electron microscope; TTC, triphenyltetrazolium chloride; UA, ursolic acid; tPA, tissue-type plasminogen activator.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intracisternal administration of tanshinone IIA-loaded nanoparticles leads to reduced tissue injury and functional deficits in a porcine model of ischemic stroke.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2021 Jan 5;10:18-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2020.11.003. eCollection 2021 Jun. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33842909 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-edema and antioxidant combination therapy for ischemic stroke via glyburide-loaded betulinic acid nanoparticles.Theranostics. 2019 Sep 21;9(23):6991-7002. doi: 10.7150/thno.35791. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31660082 Free PMC article.
-
Brain Targeting, Antioxidant Polymeric Nanoparticles for Stroke Drug Delivery and Therapy.Small. 2022 Jun;18(22):e2107126. doi: 10.1002/smll.202107126. Epub 2022 Mar 20. Small. 2022. PMID: 35306743 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic benefits of nanoparticles in stroke.Front Neurosci. 2015 May 19;9:182. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00182. eCollection 2015. Front Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26041986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in nanomedicines for the treatment of ischemic stroke.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Jul;11(7):1767-1788. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.11.019. Epub 2020 Nov 28. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 34386320 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nanotechnology approaches to drug delivery for the treatment of ischemic stroke.Bioact Mater. 2024 Sep 23;43:145-161. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.09.016. eCollection 2025 Jan. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 39386225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymeric nanocarriers delivery systems in ischemic stroke for targeted therapeutic strategies.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Jul 18;22(1):424. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02673-4. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39026255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticle-based drug delivery for the treatment of traumatic brain injury.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2023 Jan;20(1):55-73. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2023.2152001. Epub 2022 Dec 6. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2023. PMID: 36420918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances of Natural Pentacyclic Triterpenoids as Bioactive Delivery System for Synergetic Biological Applications.Foods. 2024 Jul 16;13(14):2226. doi: 10.3390/foods13142226. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39063310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Magnetic Hyperthermia Enhancement in Iron-based Materials Driven by Carbon Support Interactions.Chemistry. 2022 Dec 1;28(67):e202201861. doi: 10.1002/chem.202201861. Epub 2022 Oct 6. Chemistry. 2022. PMID: 36058884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Virani S., Alonso A., Benjamin E., Bittencourt M., Callaway C., Carson A., et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2020 update: a report from the American heart association. Circulation. 2020;141:e139–e596. - PubMed
-
- Schwamm L., Ali S., Reeves M., Smith E., Saver J., Messe S., et al. Temporal trends in patient characteristics and treatment with intravenous thrombolysis among acute ischemic stroke patients at Get with the Guidelines-Stroke hospitals. Circulation Cardiovascular quality and outcomes. 2013;6:543–549. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

