A gene network of uterine luminal epithelium organizes mouse blastocyst implantation
- PMID: 35386370
- PMCID: PMC8967306
- DOI: 10.1002/rmb2.12435
A gene network of uterine luminal epithelium organizes mouse blastocyst implantation
Abstract
Purpose: The receptive endometrium is critical for blastocyst implantation. In mice, after blastocysts enter the uterine cavities on day 4 of pregnancy (day 1 = vaginal plug), blastocyst attachment is completed within 24 h, accompanied by dynamic interactions between the uterine luminal epithelium and the blastocysts. Any failures in this process compromise subsequent pregnancy outcomes. Here, we performed comprehensive analyses of gene expression at the luminal epithelium in the peri-implantation period.
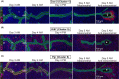
Methods: RNA-seq combined with laser microdissection (LMD) was used to reveal unique gene expression kinetics in the epithelium.
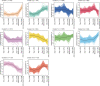
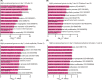
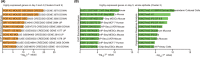
Results: We found that the prereceptive epithelium on day 3 specifically expresses cell cycle-related genes. In addition, days 3 and 4 epithelia express glutathione pathway-related genes, which are protective against oxidative stresses. In contrast, day 5 epithelium expresses genes involved in glycolysis and the regulation of cell proliferation. The genes highly expressed on days 3 and 4 compared to day 5 are related to progesterone receptor signaling, and the genes highly expressed on day 5 compared to days 3 and 4 are associated with the ones regulated by H3K27me3.
Conclusions: These results suggest that specific gene expression patterns govern uterine functions during early pregnancy, contributing to implantation success.
Keywords: blastocyst implantation; gene expression; laser microdissection; luminal epithelium; uterus.
© 2022 The Authors. Reproductive Medicine and Biology published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japan Society for Reproductive Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Human rights: This article does not contain any studies using human participants. Animal studies: The animal studies were approved by the Animal Experiment Committee of The University of Tokyo (Approval number: P16‐066; P20‐076) and performed according to the institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals.
Figures

References
-
- Huet‐Hudson YM, Andrews GK, Dey SK. Cell type‐specific localization of c‐myc protein in the mouse uterus: modulation by steroid hormones and analysis of the periimplantation period. Endocrinology. 1989;125:1683‐1690. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
