Small extracellular vesicles with nanomorphology memory promote osteogenesis
- PMID: 35386457
- PMCID: PMC8964989
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.01.008
Small extracellular vesicles with nanomorphology memory promote osteogenesis
Abstract
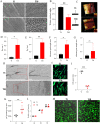
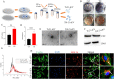
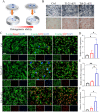
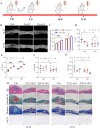
Nanotopographical cues endow biomaterials the ability to guide cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation. Cellular mechanical memory can maintain the cell status by retaining cellular information obtained from past mechanical microenvironments. Here, we propose a new concept "morphology memory of small extracellular vesicles (sEV)" for bone regeneration. We performed nanotopography on titanium plates through alkali and heat (Ti8) treatment to promote human mesenchymal stem cell (hMSC) differentiation. Next, we extracted the sEVs from the hMSC, which were cultured on the nanotopographical Ti plates for 21 days (Ti8-21-sEV). We demonstrated that Ti8-21-sEV had superior pro-osteogenesis ability in vitro and in vivo. RNA sequencing further confirmed that Ti8-21-sEV promote bone regeneration through osteogenic-related pathways, including the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway, MAPK signaling pathway, focal adhesion, and extracellular matrix-receptor interaction. Finally, we decorated the Ti8-21-sEV on a 3D printed porous polyetheretherketone scaffold. The femoral condyle defect model of rabbits was used to demonstrate that Ti8-21-sEV had the best bone ingrowth. In summary, our study demonstrated that the Ti8-21-sEV have memory function by copying the pro-osteogenesis information from the nanotopography. We expect that our study will encourage the discovery of other sEV with morphology memory for tissue regeneration.
Keywords: Nanotopographic; Osteogenesis; PEEK; Small extracellular vesicles; hMSCs.
© 2022 The Authors.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Nanotopography Sequentially Mediates Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles for Enhancing Osteogenesis.ACS Nano. 2022 Jan 25;16(1):415-430. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c07150. Epub 2021 Dec 22. ACS Nano. 2022. PMID: 34935354
-
Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Promote Periodontal Regeneration.Tissue Eng Part A. 2021 Jul;27(13-14):962-976. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2020.0141. Epub 2020 Nov 23. Tissue Eng Part A. 2021. PMID: 32962564
-
MSC-derived small extracellular vesicles overexpressing miR-20a promoted the osteointegration of porous titanium alloy by enhancing osteogenesis via targeting BAMBI.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Jun 16;12(1):348. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02303-y. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34134765 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of nanofibers on mesenchymal stem cells: environmental factors affecting cell adhesion and osteogenic differentiation and their mechanisms.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2020 Nov.;21(11):871-884. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2000355. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2020. PMID: 33150771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles and bone regeneration.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021 Jan;128(1):18-36. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.13478. Epub 2020 Sep 22. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 32780530 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Potential of Nano-Engineered Stem Cells in the Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis: A Comprehensive Review.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Dec 17;44(1):6. doi: 10.1007/s10571-023-01434-5. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 38104307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles: From bone development to regenerative orthopedics.Mol Ther. 2023 May 3;31(5):1251-1274. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.02.021. Epub 2023 Mar 3. Mol Ther. 2023. PMID: 36869588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered exosomes: a promising strategy for tendon-bone healing.J Adv Res. 2024 Oct;64:155-169. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.11.011. Epub 2023 Nov 14. J Adv Res. 2024. PMID: 37972886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifaceted Materials for Enhanced Osteogenesis and Antimicrobial Properties on Bioplastic Polyetheretherketone Surfaces: A Review.ACS Omega. 2024 Apr 12;9(16):17784-17807. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c00923. eCollection 2024 Apr 23. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38680314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioengineering extracellular vesicles: smart nanomaterials for bone regeneration.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Apr 27;21(1):137. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-01895-2. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 37106449 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang X., Xu M., Song L., Wei Y., Lin Y., Liu W., Heng B.C., Peng H., Wang Y., Deng X. Effects of compatibility of deproteinized antler cancellous bone with various bioactive factors on their osteogenic potential. Biomaterials. 2013;34:9103–9114. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.08.024. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ma L., Feng X., Liang H., Wang K., Song Y., Tan L., Wang B., Luo R., Liao Z., Li G., Liu X., Wu S., Yang C. A novel photothermally controlled multifunctional scaffold for clinical treatment of osteosarcoma and tissue regeneration. Mater. Today. 2020;36:48–62. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2019.12.005. - DOI
-
- Zhang T., Wei Q., Zhou H., Jing Z., Liu X., Zheng Y., Cai H., Wei F., Jiang L., Yu M., Cheng Y., Fan D., Zhou W., Lin X., Leng H., Li J., Li X., Wang C., Tian Y., Liu Z. Three-dimensional-printed individualized porous implants: a new "implant-bone" interface fusion concept for large bone defect treatment. Bioact. Mater. 2021;6:3659–3670. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.03.030. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fitzpatrick V., Martin-Moldes Z., Deck A., Torres-Sanchez R., Valat A., Cairns D., Li C., Kaplan D.L. Functionalized 3D-printed silk-hydroxyapatite scaffolds for enhanced bone regeneration with innervation and vascularization. Biomaterials. 2021;276:120995. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.120995. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

