Hypersensitivity to Gadolinium-Based Contrast Media
- PMID: 35386665
- PMCID: PMC8974732
- DOI: 10.3389/falgy.2022.813927
Hypersensitivity to Gadolinium-Based Contrast Media
Abstract
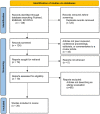
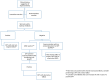
Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) are frequently used in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examinations to increase sensitivity in diagnoses. Recently, an increase in the description of hypersensitivity reactions to GBCAs has been detected. We performed research in PubMed, PubMed, SCOPUS, and EMBASE until September 2021, searching for studies regarding immediate and delayed hypersensitivity reactions to gadolinium-based contrast agents in which an allergy study was performed. The initial research identified 149 articles written in English. After excluding articles duplicated and articles that had irrelevant designs, 26 articles were included. Finally, 17 studies concerning immediate reactions, six studies concerning non-immediate reactions, and three concerning both that performed allergy evaluations were selected. In the review, we analyzed the characteristics of immediate and delayed reactions and the results of the allergy study and cross-reactivity. Skin tests seem to have acceptable accuracy, but drug provocation tests are still needed when skin tests are negative o to find alternative agents. Although cross-reactivity patterns are not well established, cross-reactivity seems to exist among macrocyclic agents. Notwithstanding, the number of patients analyzed is low and further studies are required. A management algorithm is suggested.
Keywords: allergy; gadolinium based contrast agent; hypersensitivity; immediate reactions; non-immediate reactions; skin test.
Copyright © 2022 Gracia Bara, Gallardo-Higueras, Moreno, Laffond, Muñoz Bellido, Martin, Sobrino, Macias, Arriba-Méndez, Castillo and Davila.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Balzer T. Presence of gadolinium (Gd) in the brain and body. Presentation to the medical imaging drugs advisory committee. New York, NY: United States Food and Drug Administration, Silver Spring. (2017).
-
- Weinreb JC, Rodby RA, Yee J, Wang CL, Fine D, McDonald RJ, et al. . Use of intravenous gadolinium-based contrast media in patients with kidney disease: consensus statements from the American College of Radiology and the national kidney foundation. Kidney Med. (2021) 3:142–50. 10.1016/j.xkme.2020.10.001 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

